| Culture | Culture denotes ‘the way of life’ of a society or group of people. It is a paradigm that filters our ability to interpret the world. We can easily distinguish between British, American and Indian cultures by spoken and body language, beliefs, habits and cuisine. Culture can be defined as the set of shared and inherited ideas, attitudes, values, practices, beliefs and cumulative experiences and knowledge that determine social action, sense of individual identity and people’s attitude to interpret the world. |
| Cultural traits | Denote the features or characteristics of a culture, recognized in terms of language, customs, traditions, beliefs or faith, dress, music, images, food, festivals and even appearance. |
| Cultural ethnocentrism | It is the belief that one’s own culture is superior to that of other cultures. It is a form of reductionism that reduces the “other way” of life by interpreting it from one’s own perspective. |
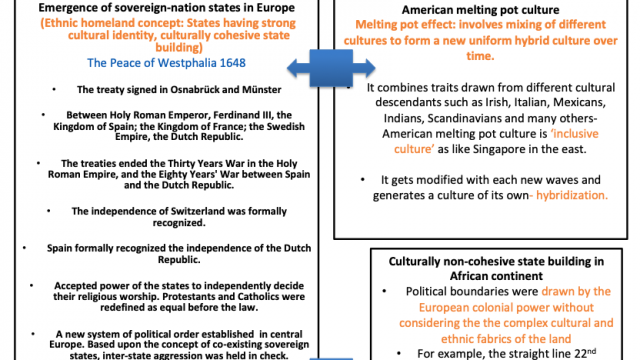
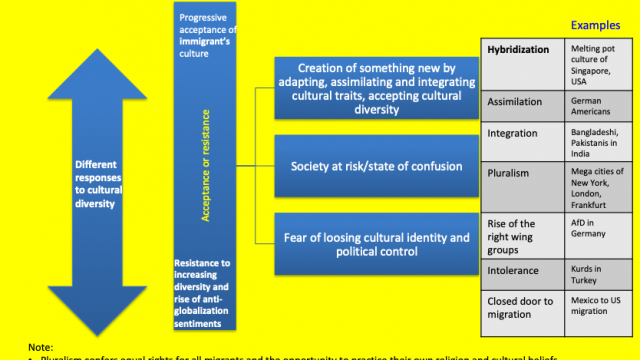
| Cultural hybridization | Mixing or blending of different cultural traits and elements of different cultures and the consequent emergence of a new, unique culture. Language and music are the most common examples of hybridization in the globalized world. Many African countries speak french and mix it in with their native language, creating new lexicon. US pop music mixing with South Korean music such as K-pop group, South Korean boy band BTS symbolizes cultural hybridization. |
| Cultural diffusion | It is the process of spreading of one mainstream culture from it’s origin to another place. Cultural traits can be diffused both in real or virtual space (cyberspace) in a number of ways such as mass tourism, movement of workers or migrants, through trade and spread of transnational corporations. For example, Indian restaurants in London or New York. Two of the popular Hollywood films in the U.S. “Hidden Dragon” and “Mulan” were originally adapted from China. |
| Cultural dilution | Cultural dilution signifies the weakening of the mainstream cultural traits as a result of diffusion and contact with other cultures. |
| Cultural homogenization or convergence | Mixing of different cultures that results in the rise of single-common global culture. It refers to the reduction in cultural diversity. |
| Cultural imperialism | Imposition of one culture upon another with articulated purposes such as capturing of market by spreading consumerism or reshaping of popular consciousness to establish hegemonic control. ‘Americanization’ is recognized as a kind of cultural imperialism. Cultural imperialism can also take the form of neo-colonialism or cultural colonialism |
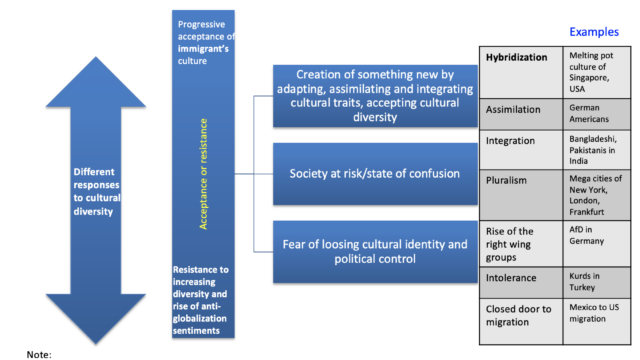
| Cultural diversity | Variations and coexistence of different cultures over a particular space or territory. |
| Diaspora | Diaspora denotes the stream of scattering or large scale dispersal of a community of people sharing a common cultural and/or geographic origin from its original homeland to other parts of the world. rish Diaspora is another significant historic diaspora in the world peaked up during the great famine in 1845. Nearly 70 million people worldwide claim Irish descent today (much more than the total population of the Republic of Ireland). In the United States, Irish is the second most common ancestry after Germans. |
| Branded commodities | Brand is a distinguishing name or symbol associated with the identity of a product, service or company. Strong brands have the power to create considerable competitive and comparative advantage and can increase the revenue by ensuring high demand and market share. |
| Glocalization | Emphasizes that the globalization of a product is more likely to succeed when the product or service is adapted specifically to each locality or culture in which it is marketed. The increasing presence of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide is an example of globalization, while changes made to the menus of the restaurant chain in an attempt to appeal to local tastes, are an example of glocalization. For example, McDonald’s in India serves Vegetable McNuggets (instead of chicken base) and Mutton based Maharaja Mac (instead of beef base Big Mac) as religious norms prohibit Hindus (80% of India’s popular are Hindus) to eat beef. |
| Ethnicity and Identity | The shared identity of an ethnic group based on common ancestral roots or cultural characteristics such as language, religion, diet or place of origin. Identity is related to the sense of attachment or belongingness of an individual or society. |
| Minority group | A minority group is any category of people who are differentiated from the social majority in a country or community. A person may be in a minority group because of their age, caste, ethnicity, gender, health, language, race, physical condition, religion, sexual orientation, or wealth. |
Processes and Sources of Cultural Diffusion (how does culturural diffusion occur?)
| Historic | Exploration and discoveries of the land. Establishment of trading link and search of the raw material sources Colonization | Diffusion through expansion, mainly using hard powers or military forces (spread into new areas other than the original core or source of the culture) |
|---|---|---|
| Economic | Trade relationship and expansion of market. Labour movement and search for better opportunities - Migration Foreign direct investment and outsourcing Advertising and role of the global media. | Both expansion and diffusion through relocation (People or migrant workers spread the culture along with them) |
| Socio-cultural | International Tourism Global social media | Diffusion through conduction of cultural traits in the virtual world (with out direct contact but through news, music, movies, advertisement) |
| Post-modern phenomena | Neo-imperialism Americanization/westernization | Diffusion through expansion but without force, mainly using soft powers. |
Diaspora:
Diaspora denotes the stream of scattering or large scale dispersal of a community of people sharing a common cultural and/or geographic origin from its original homeland to other parts of the world. The term was originally related to the historic dispersal of the Jewish people after the expulsion from the Kingdom of Israel in in 733 BCE. Jews are largely concentrated (refer to the Pew Research centre report) in North America (44%) and in the Middle East and North Africa region (41%). Most of the remainder of the Jewish population was found in Europe (10%) and the Latin America-Caribbean region (3%). Irish Diaspora is another significant historic diaspora in the world peaked up during the great famine in 1845. Nearly 70 million people worldwide claim Irish descent today (much more than the total population of the Republic of Ireland). In the United States, Irish is the second most common ancestry after German.
Forced Diaspora: Another major example of historic diaspora is related to the slave trade of around 12 million Africans to North and South America including the Caribbean region by the European colonizers to work in the sugar and cotton plantation. This diaspora is related to the emergence of the concept of racial inferiority between the slave owing elite colonizers and the victims Africans.
With 17.5 million migrants in 2018, Indian diaspora is the world largest. Read the recent report to analyze the extent of Indian diaspora.
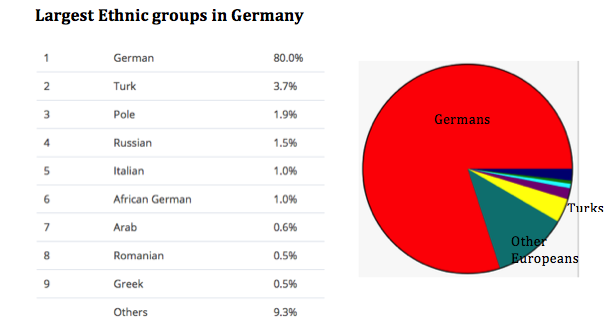
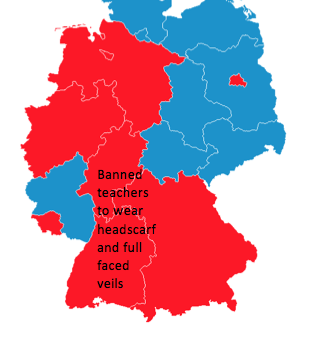
Turks make up Germany’s largest ethnic minority since 1961, still not integrated with the German mainstream culture:
Some fundamentals of Turkish culture
Impact of Brexit: Read Guardian report on worry about the returns of the Polish workers to the higher wages areas of East and how it may impact UK.
The Role of Diaspora: How diasporas influence cultural diversity and identity?
Using examples, analyze the influence of diaspora populations on the cultural identity of different places. (N2019)
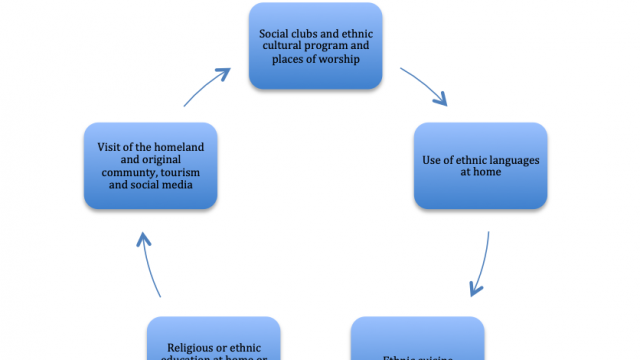
Ethnic Villages: Shaping up the cultural traits over the built-up landscapes of the world cities
These are the evidences of the minority groups residing in certain location marked by their own cultural traits in terms of shops, schools, places of worship etc. For example, the German school in Richmond and the nearby German bakery in London have become the key reference point for the German community in London.
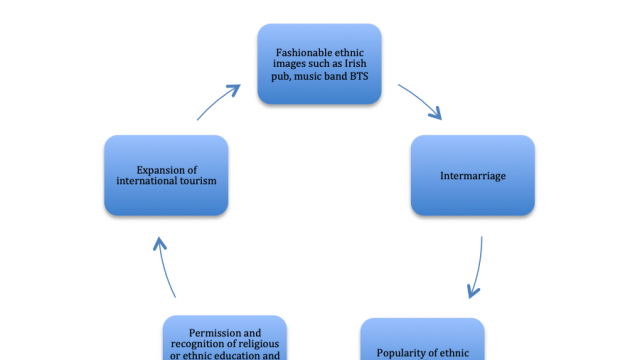
Adoptation of minority traits by the host society:
Adoptation may lead to multiculturalism and integration also propelled by the rapid expansion of international tourism in the recent decades. For example, in UK and USA children learn about other cultures in a number of subjects and thus have a better understanding of different cultures than previous generations. Understanding of cultural differences reduce barriers to the adoptation of minority traits due to appreciation of the positive elements of the alternative cultures.