Analyze data using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (rho)
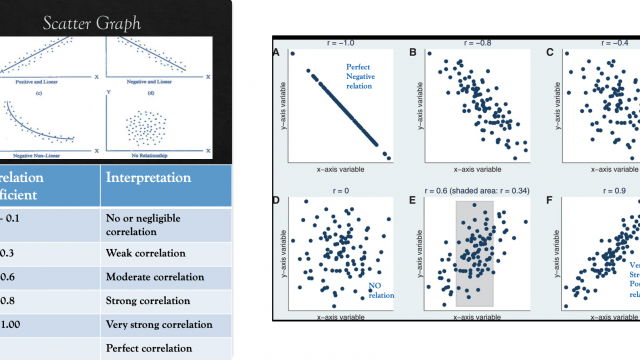
- It measures the relationship between two logically related variables. Like the conventional correlation coefficient (r), Spearman rho can have any value between -1 to +1. A Spearman correlation of 1 results when the two variables being compared are monotonically related, even if their relationship is not linear. In a monotonic relationship, the variables tend to move in the same relative direction, but not necessarily at a constant rate. Monotonic relationship can be nonlinear. In a linear relationship, the variables move in the same direction at a constant rate.
CLICK HERE to refer to the diagrams of Linear, Nonlinear and monotonic relationships.
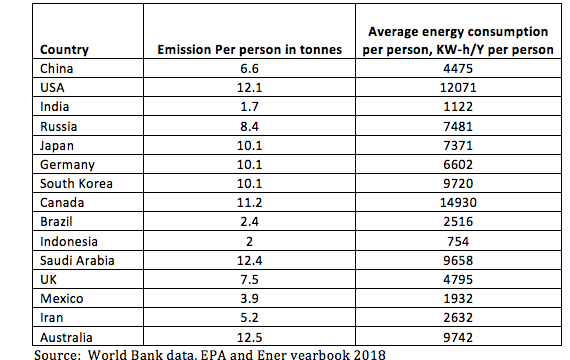
In Statistics, Correlation is largely a measure of an association between variables. In logically correlated data, the change in the magnitude of 1 variable is related to a corresponding change in the magnitude of another variable, either in the same (positive correlation: High-High, Low-Low) or in the opposite (negative correlation: Low-High or High-Low) direction. Very often, the term correlation is used in the context of a linear relationship between 2 continuous variables and expressed as Pearson product-moment correlation. For monotonically (nonlinear) distributed continuous ordinal data(indicate the order or rank of things) or for data with relevant outliers, Spearman rank correlation can be used as a measure. Spearman rho refers to the ranked values rather than the original measurements.
| Variable A (arranged in an ascending order-smallest to largest) | Rank (R1) (assigned after arranging in order) | Variable B | Rank (R2) | Difference in rank (R1-R2)=d | d² |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 10 | 6.2 | 1 | +9 | 81 |
| 1100 | 9 | 5.1 | 2 | +7 | 49 |
| 1900 | 8 | 3.1 | 4 | +4 | 16 |
| 2400 | 7 | 4.6 | 3 | +4 | 16 |
| 3100 | 6 | 2.5 | 5 | +1 | 1 |
| 3900 | 5 | 1.5 | 7 | -2 | 4 |
| 4200 | 4 | 1.8 | 6 | -2 | 4 |
| 5300 | 3 | 0.4 | 10 | -7 | 49 |
| 5900 | 2 | 1.3 | 8 | -6 | 36 |
| 6500 | 1 | 0.5 | 9 | -8 | 64 |
| Total d² = 320 |
Spearman rank ![]()
where n = number of paired observations
![]()
![]()
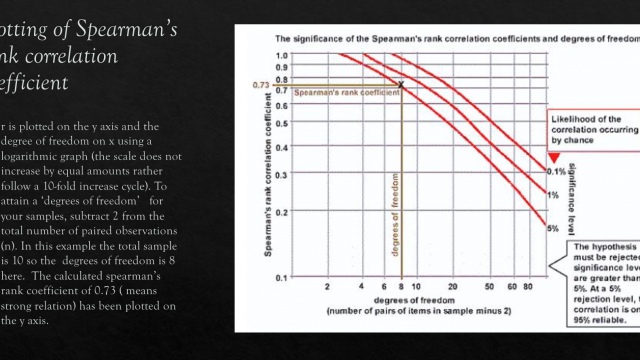
There are (n) degrees freedom (10)
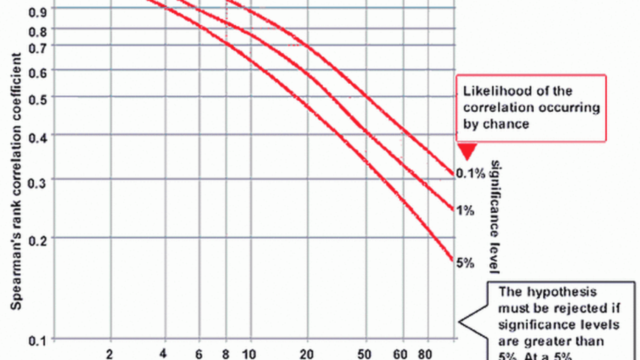
Significance Level
Compare your result to the critical values for Spearman's Rank correlation (ignoring + / -). If rho is greater than or equal to the critical value, then there is a significant correlation and the null hypothesis can be rejected.| Number of pairs of measurement (n) | p = 0.05 (95%) (+ or -) | p = 0.01 (99%) (+ or -) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | |
| 6 | 0.886 | 1.000 |
| 7 | 0.786 | 0.929 |
| 8 | 0.738 | 0.881 |
| 9 | 0.683 | 0.833 |
| 10 | 0.648 | 0.818 |
| 11 | 0.623 | 0.794 |
| 12 | 0.591 | 0.780 |
| 13 | 0.566 | 0.745 |
| 14 | 0.545 | 0.716 |
| 15 | 0.525 | 0.689 |
| 16 | 0.507 | 0.666 |
| 17 | 0.490 | 0.645 |
| 18 | 0.476 | 0.625 |
| 19 | 0.462 | 0.608 |
| 20 | 0.450 | 0.591 |
| 25 | 0.400 | 0.526 |
| 30 | 0.364 | 0.478 |
| 35 | 0.336 | 0.442 |
| 40 | 0.314 | 0.413 |
Referencing format/ Citation Style/ How to write bibliography?
How to write Bioliography: Click here to refer Harvard citation style
What is not included in Harvard Citation?
What you include depends on the citation style. Chicago A, OSCOLA, Turabian require the use of footnote citations instead of author-date in-text citations. How to insert footnotes using MS Word?

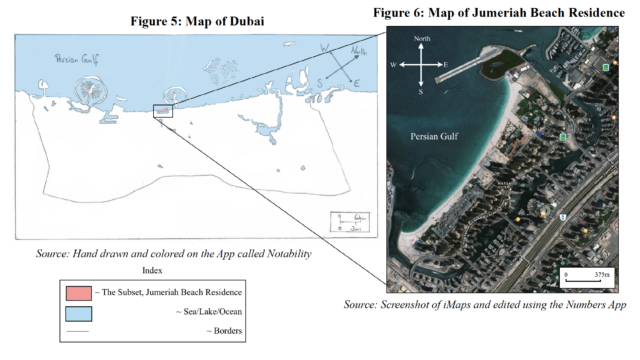
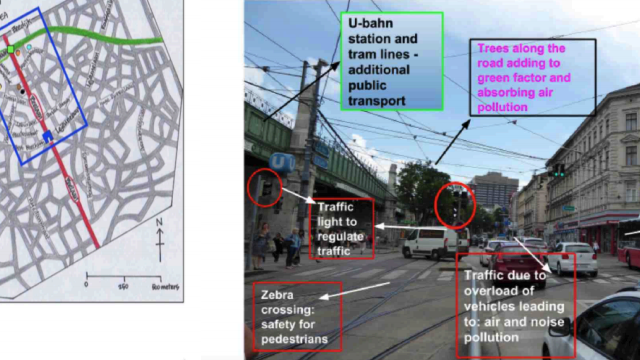
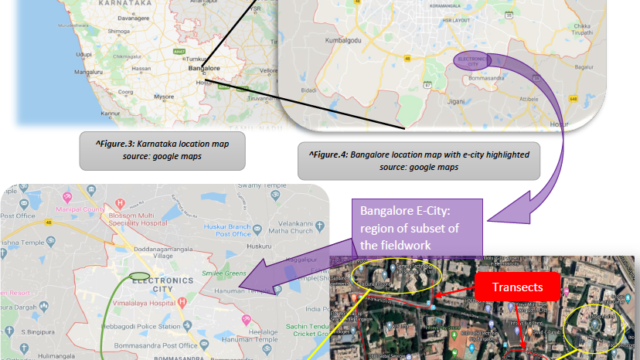
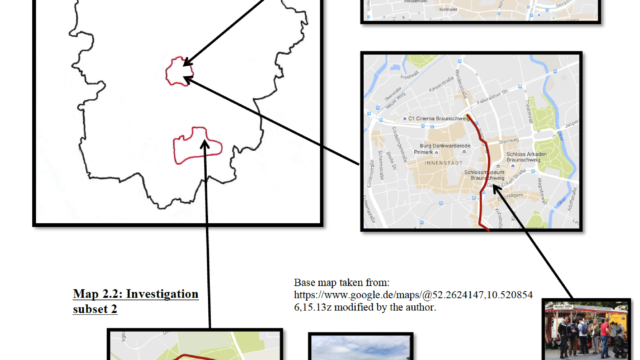




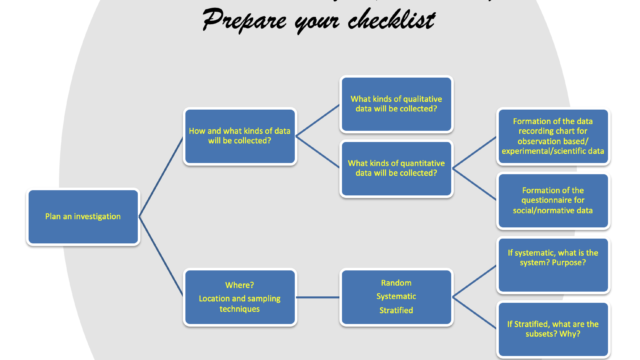
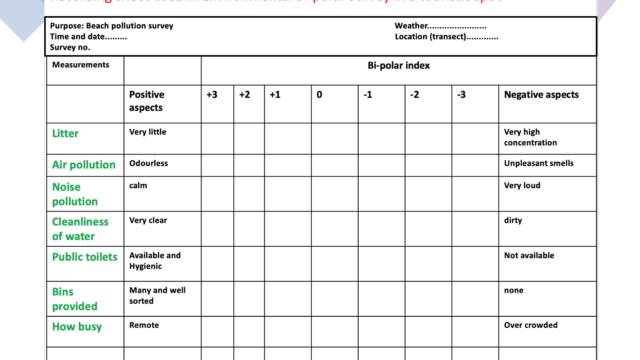
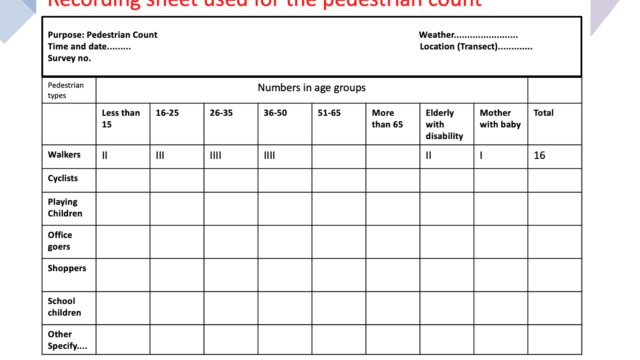


Try out your own Choropleth mapping
Download license free photos
Access maps of the world for your presentations