Hover Box Element
Hover Box Element
The Amazon Rainforest is a vast region that spans eight rapidly developing countries: Brazil, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, covers some 40% of the South American continent. Most scientists agree that the Amazon is the world’s second longest river after the River Nile.
It is the largest tropical rainforest in the world that provides 20% of the Earth’s oxygen. It’s incredibly rich ecosystem supports an estimated 30% of the world’s species, with a new species being discovered on average every 3 days. More than 80% of the world’s food has its origins in the Amazon rainforest. 25% of all western pharmaceuticals come from rainforest-based ingredients, yet less than 1% of the trees and medical plants in the Amazon rainforest have ever been tested by scientists.
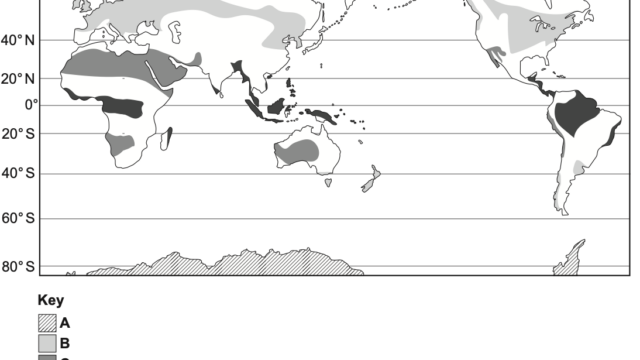
Distribution of the Tropical Rainforest
The tropical rainforest is one of the largest terrestrial biome on the earth. It is the most productive and diverse ecosystem on land. It contains over 50% of world’s species in just 7% of land. Tropical rainforests accounts for 80% of world’s insect and 90% of primates. Rainforest once covered almost 15% of the earth’s land, now has declined to only 6% due to wide spread clearance. Over 200 million people live in the rain forest. The annual loss of rainforest is about 30-40 million acres (almost the size of England). In general rainforest is disappearing at one acre per second (1 acre = .0040 sq km). According to WWF (World Wide Fund for Nature) 12-15 million hectares (1 hectare = .01 sq.km) of forest are lost each year, equivalent of 36 football fields per minute. The Amazon rainforest in South America is by far the world’s largest rainforest, covers the Amazon river basin. Over half of the forest lies in Brazil, which holds about one-third of the world’s remaining rainforest. About 13% of the Amazon rainforest is in Peru and remaining smaller areas in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Guyana and Suriname.Central America- The main areas of existing rainforests are Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras, Belize, southern Mexico, some islands in the Caribbean.Africa, Congo basin- central Africa holds the world second largest rainforest in Cameroon, Democratic Republic of Congo, Equatorial Guinea and Gabon. South-East Asia- India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia. Nearly 85% of the island of Papua New Guinea is covered by rainforest. Australia– north eastern coastal zone of North Queensland coast.
Click here to find out Countries with the largest rainforest coverage.
- State the location of the two different types of rainforests.
- Explain two benefits of the rainforest’s rich biodiversity.
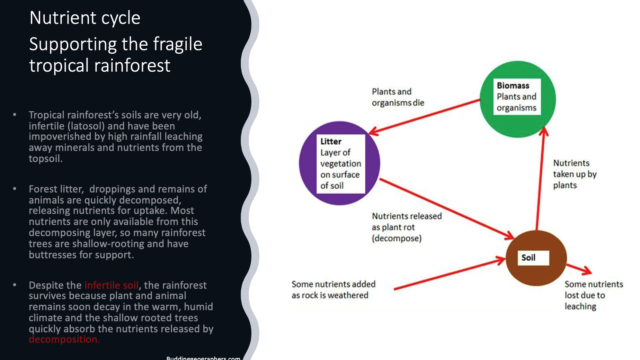
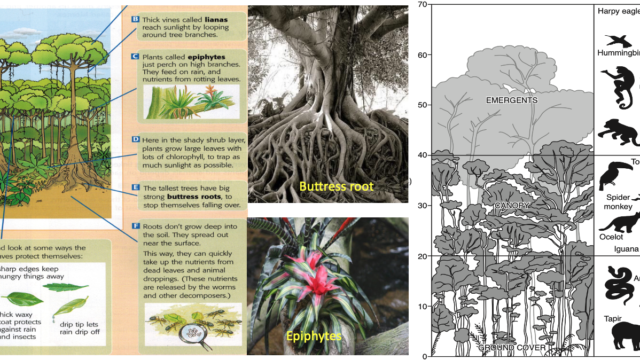
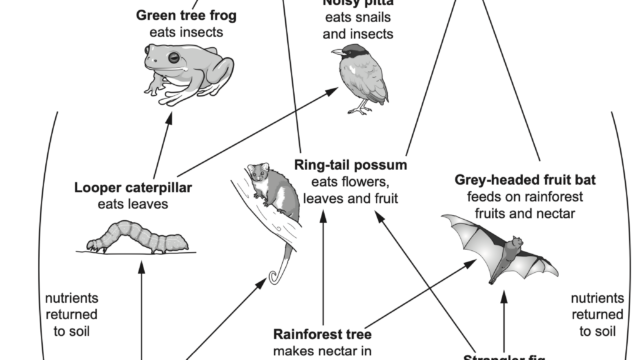
- Explain Two different examples of the relationship between the plants and the animals in the tropical rainforest ecosystem. How are they helping each other to thrive in the jungle even though the soil is infertile?
- Mention one of the threats (refer to the specific example) to the biodiversity of the tropical rainforest.
Photo Gallery
Photographs of Rainforest on National Geographic
National Geographic photo gallery on Tropical Rain forest wildlife
Deforestation in photographs by National Geographic
Virtual Field trip
NatureLab: Virtual Field trip to Borneo’s tropical rainforest
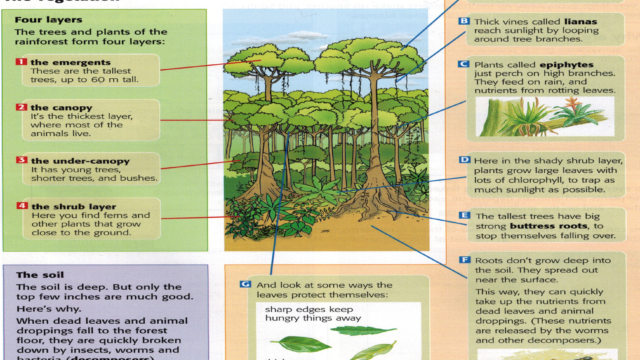
Layers of the Tropical Rainforest and the unique Ecosystem
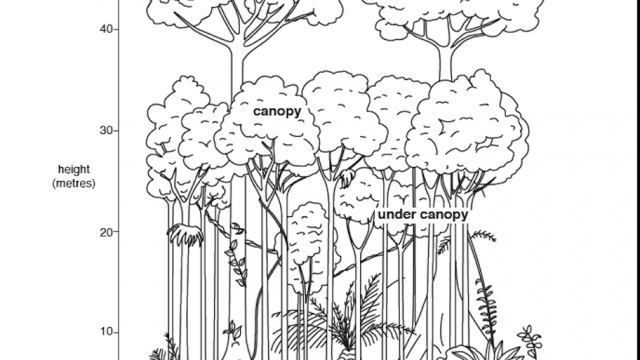
1. What are the 4 major layers of the tropical rainforest? ( NatureLab: Virtual Trip to Amazon Rainforest.…learn about the forest layers)
2. Identify the type of trees which grow over 40 meters tall.
3. Note down two animals that are found in distinct layers of the rainforest.
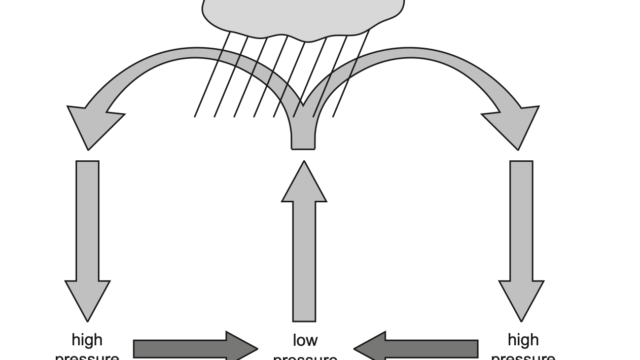
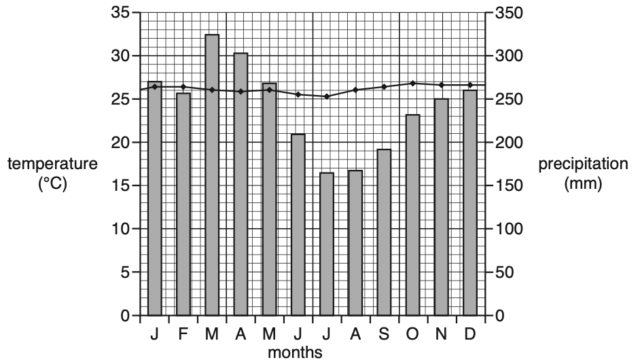
4. Describe the characteristics of the tropical rainforest using the climate graph. Use statistics to support your answer.
Practice Test 1: Interactive Video on Tropical Rainforest
Thanks to Bethany Randall on Unsplash for the photos
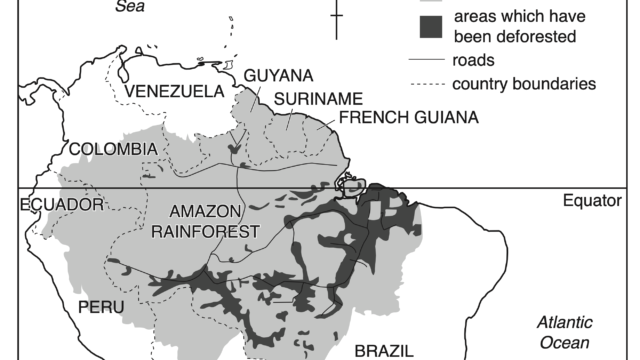
Deforestation
Source: FAO Infographic: http://www.fao.org/resources/infographics/infographics-details/en/c/325836/