Thought Provoking Facts on Inequality
- At least 80% of humanity lives on less than $10 a day. The world’s wealthiest countries with approximately 1 billion people accounted for 76% of the world’s GDP.
- The world’s billionaires (just 500 people) are holding over 7% of world GDP.
- More than 1 billion people live in water-scare regions. Agriculture is responsible for about 70% of global water withdraws and 24% of human generated greenhouse gas emissions.
- 1.3 billion people worldwide lack access to electricity needed to raise their standard of living.
- Some 1.1 billion people in developing countries have inadequate access to water, and 2.6 billion People lack basic sanitation in the world.
- Nearly 800 million people around the world are undernourished and nearly 300 million children go to bed hungry every day while 1.4 billion are overweight.
- According to FAO, 25,000 children die each day due to poverty. Nearly 14 children are dying every minute.
- Nearly a billion people entered the 21st century unable to read a book or sign their names. However, less than one per cent of what the world spent every year on weapons was needed to put every child into school by the year 2000 and yet it didn’t happen.
- More than half the global population lives in the cities (54% of the world’s population). Nearly 1 billion of them are living in the slums.
- Some 46-58 thousand square miles of forest are lost each year, equivalent to 38 football fields every minute. It is estimated that 15% of all greenhouse gas emissions are the result of deforestation (WWF)
- Every 4 seconds one person dies of starvation. Usually it is a child under the age of 5
What is development?
- Development is about improving people’s lives to ensure quality of life while promoting human dignity and respect. It means positive change for betterment.
- It means more equal society, justice for everyone, chance to earn a good living and ability to meet the basic needs of life in terms of access to food, water, sanitation, quality education, health services.
- Development is about finding ways to live sustainably
- Development is not purely an economic phenomenon but a multi-dimensional process involving reorganization and reorientation of the entire economic and social system
- Expansion of human freedom should both be viewed as the primary end and the principle means of development (views of Prof. Amartya Sen in his book Development as Freedom. Sen received Nobel prize in Economics for his contribution in developmental studies)
Objectives of Development
- Raising peoples’ living standards, i.e. incomes and consumption, level and quality of food consumption, access to medical services and education.
- Establishment of social, political and economic justice.
- Increasing peoples’ freedom to choose by enlarging the range of choices.
Paradoxes
- ‘Development’ is a concept which is contested both theoretically and politically, and is inherently both complex and ambiguous’.(Thomas, 2004: 1, 2)
- ‘If development means good change, questions arise about what is good and what sort of change matters‘…(Chambers, 2004: iii, 1–2)
- ‘Since development depends on values and on alternative conceptions of the good life, there is no uniform or unique answer’. (Kanbur, 2006: 5)
Developmental Approaches (How to stimulate development in a country)
Top down development: Require large scale State (public) investment
- This is usually large scale development, carried out by government or international organization
- It is done by people from outside area/ it is imposed upon the area or people by outside organization
- It is often well funded and can respond quickly to disaster eg. Aswan Dam, or emergency relief
- The local people are hardly involved in the decision making process
Bottom-up development: Social entrepreneurship approach
- It is small scale and mostly labour intensive
- It involves local communities and local people eg. building earth dam, cottage industries
- The local people are involved in decision making process
- Run by the local communities for the local people eg. Grameen bank of Bangladesh
Sustainable development: Environmental, economic and social well-being for today and tomorrow
Sustainable development has been defined in many ways, but the most frequently quoted definition is from Our Common Future, also known as the Brundtland commission Report, 1987 (Geo Harlem Brundtland, former prime minister of Norway, Headed the commission) to the World Commission on environment and development.
“Sustainable development.. is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs. (Brundtland commission Report, 1987)
Muhamad Yunus received Nobel Price Prize in 2006 for his profound contribution to the development of the rural areas of Bangladesh through Grameen Bank efforts. Here is the link of the Nobel Prize Committee on the facts of the Grameen Bank effort.
Multi-dimensional process of human development and ways to measure
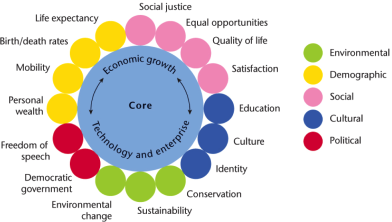
Different countries of the world are classified according to their level of social and economic development. Levels of development are dependent on physical or environmental, economic, demographic, socio-cultural and political factors. Development involves complex series of interlinked processes (refer to the development cable diagram).
Purely Economic Measures:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total economic output of a country in a year. It is the total value of all final goods and services produced within an economy over a period of time, usually a year. GDP is an indicator of the local/national economy.
GDP per capita to understand how the wealth is distributed within the population, however as it is an average, extreme rich and poor will be neutralized by the result. GDP per capita is the total output divided by the total number of people or population, i.e. the average amount of money each person makes.
Gross National Product (GNP): GNP is the total value of all the goods and services produced domestically and abroad by the citizen’s of a country. GNP represents how the nationals of a country are contributing to the country’s economy giving importance to citizenship but overlooks location.
Gross National Income (GNI): The total value of goods and services produced in a country (i.e. GDP), together with the balance of income and payments from or to other countries (including interest payment and dividends). GNI per person provides a better picture of the wealth distribution.
Better solution to GNI measure is to consider GNI at PPP:
Purchasing power parity (PPP): Is the measure of the average earnings in relation to local prices (i.e. how much one can buy in local currency equivalent to 1 dollar). PPP is a macroeconomic approach to compare economic productivity and standards of living between countries. It is based on “basket of goods” approach to compare the buying power of a local currency. The GNI of a country is converted into US dollars on the basis of how the value of a currency can be compared to other countries in relation to the buying power of the currency. PPP is calculated by comparing the price of good ‘X’ in different countries. To make a meaningful comparison of prices across countries, a wide range of goods and services must be considered. The popular “Big Mac Index” (the price of Big Mac hamburger across many countries) is popularly used to compare PPP in many cases.
Why only economic indicator is not reliable to measure development or disparities?
- These measures are purely economic and are not composite indicator. They do not provide any idea of human capital formation (education, training, health condition), gender equality, and condition of human rights. Even as an economic indicator it is not a holistic one as it does not include the income generated by the informal economy, which plays a significant role in many developing countries.
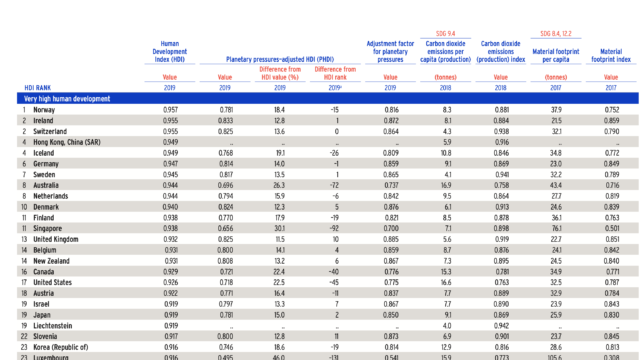
- There are alternative well developed composite measures available since 1990s like HDI including GDI etc that measures average achievements of the population in terms of health, education and access to goods and services.
Click here to see Ranking of world’s Economies based on GDP and PPP
Composite Indices
HDI was devised by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in 1990s and has been in use in its current form since 2010. HDI is a composite indicator that ranks countries from 0 to 9 index values based on the following criteria.
Economic Criteria : Gross National Income per capita adjusted for purchasing power parity
Social Criteria: life expectancy and literacy.
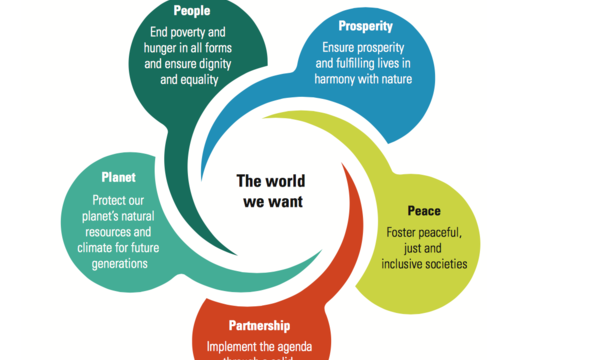
The Sustainable Development Goals are the blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all. They address the global challenges we face, including those related to poverty, inequality, climate, environmental degradation, prosperity, and peace and justice. The Goals are interconnect and in order to create a better world for every one, it ís important that we achieve each Goal and target by 2030. Click here to read more about the UN Sustainable Development Goals criteria.
The origins of the Human Development Index (HDI)
- First incorporated in the UNDP annual Development report developedby Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq in 1990 with the explicit purpose “to shift the focus of development economics from national income accounting to people-centered policies”.
- He was influenced by Nobel laureate Amartya Sen’s work on welfare economics who visualizes Development as the expansion of people’s freedom.
Strength of HDI
- A composite index measuring average achievement in three basic dimensions of human development
- Life expectancy index: Life expectancy at birth
- Education index: Mean years of schooling and expected years of schooling
- A decent standard of living measured by considering GNI per capita adjusted to PPP in US$
HDI is even stronger composite index since 2010:
In the 2010 Human Development Report a further Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI) was introduced, proving a greater stress to measure gender inequality by incorporating GDI (Gender related development index) which is basically HDI adjusted for gender inequality.
- It allows comparison between countries with changes in these components over time since 1990. Therefore, the Human Development Index (HDI) is a comparative measure of life expectancy, literacy, standards of living, and quality of life for countries worldwide.
- It is a standard means of measuring human well being. It is frequently used to distinguish whether the country is a developed, a developing or an underdeveloped country, and also to measure the impact of economic policies on the quality of life.
Gender Development Index (GDI)
The GDI is the ratio of the HDIs calculated separately for females and males using the same methodology as in the HDI. It is a direct measure of gender gap showing the female HDI as a percentage of the male HDI.
Gender Inequality Index (GII) based on UNDP report
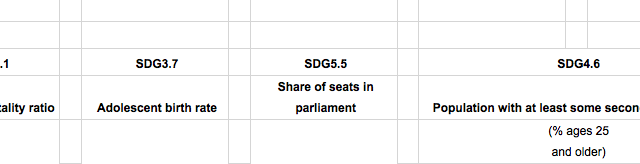
Gender inequality remains a major barrier to human development. Women and girls are often discriminated against in health, education, political representation, labour market with negative consequences for development of their capabilities and their freedom of choice. Girls and women have made major strides since 1990, but gender equity still is a distant fact. The GII is an inequality index. It measures gender inequalities in three important aspects of human development—reproductive health, measured by maternal mortality ratio and adolescent birth rates; empowerment, measured by proportion of parliamentary seats occupied by females and proportion of adult females and males aged 25 years and older with at least some secondary education; and economic status, expressed as labour market participation and measured by labour force participation rate of female and male populations aged 15 years and older.
Introduction of The Gender Social Norms Index in the 2019 Human Development Report
Measuring biases, prejudices and beliefs , comprises four dimensions— political, educational, economic and physical integrity. Click here to refer
Reference and sources of data: http://hdr.undp.org/en/composite/GII and http://www.economicsdiscussion.net/gender/gender-related-development-index-gdi/11904
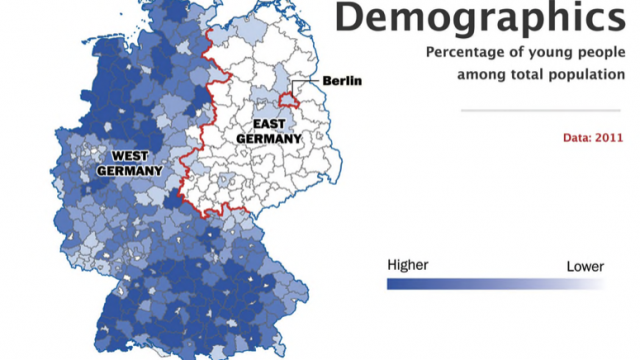
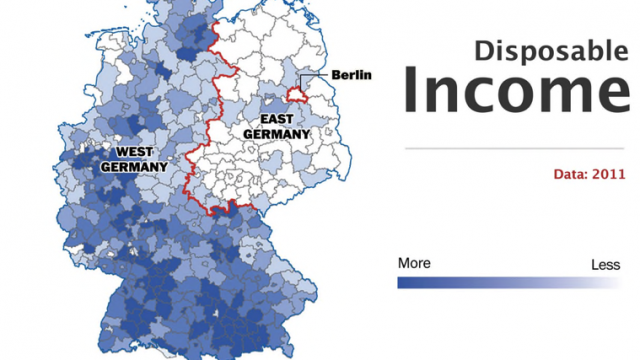
https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/worldviews/wp/2014/10/31/the-berlin-wall-fell-25-years-ago-but-germany-is-still-divided/
What is the nature of the ‘development gap’? How has it arisen? How can we measure the global development gap and what are the impacts of using different measurements?
Read here the DW report on East-West development divide in Germany
What are the roles of the different international organization in development? Click here to read more
Yet Another Measure That Matters – Happy Planet Index or HPI
The Happy Planet Index measures sustainable wellbeing for all. It tells us how well nations are doing at achieving long, happy, sustainable lives. Wealthy Western countries, often seen as the standard of success, do not rank highly on the Happy Planet Index. Instead, several countries in Latin America and the Asia Pacific region lead the way by achieving high life expectancy and wellbeing with much smaller Ecological Footprints. The Happy Planet Index provides a compass to guide nations, and shows that it is possible to live good lives without costing the Earth.
| Terminology | Explanations |
|---|---|
| What does woman Empowerment mean? What are the components of woman empowerment? | According to UNFPA, woman empowerment means- 1. Improvement of their political, social, economic and health status 2. Full participation and partnership of both women and men is required in productive and reproductive life and essential to the achievement of sustainable development goals. Countries should act to empower women and should take steps to eliminate inequalities between men and women by promoting the fulfilment of women's potential through education, skill development and employment, assisting women to establish and realize their rights, eliminating violence against women and discriminatory practices by employers against women. 3. Governments should take every possible action to remove all gender gaps and inequalities pertaining to women’s livelihoods and participation in the labour market. |
| Indigenous group Remote societies? | Indigenous people are the original settlers of the land, predating any arrival of the recent migrants into their territory. Globally, around 400 million people in 70 countries can be identified as indigenous people (nearly 5% of the world’s population). • Indigenous people generally display close community ties and a close connection to the local ecosystem. Remote societies are the indegenous people of an area but mostly uncontacted and isolated communities. These are the communities that live without significant contact to the globalized world. Uncontacted communities are mostly located in densely forested areas in central Africa, Asia, Papua New Guinea and in South America, particularly separated by geographical barriers like dense forest, vast stretch of ocean such as islands at the considerable distance from the main land etc. The Sentinelese of Andaman Nicobar Island in India still continues to reject contact with other people. |
| Minority group What does ethnicity mean? | Sociologist Louis Wirth (1945) defined a minority group as “any group of people who, because of their physical or cultural characteristics, are singled out from the others in the society in which they live. Minority group may include ethnic groups. Ethnicity is a term that describes shared culture such as the practices, values, and beliefs of a group. This culture might include shared language, religion, and traditions, among other commonalities. Minority group may become the subject of collective discrimination, differential and unequal treatment by the dominant group, who constitutes the majority. Sociologists indicate that ‘Race’ is fundamentally a social construct. Ethnicity is a term that describes shared culture and national origin. Minority groups are defined by their lack of power. America’s ethnic landscape includes African American, Hispanic, Asian, and American Indian and a rapidly growing Arab population, a sizeable Jewish population. Native Americans are also divided in their beliefs, contributing to the melting pot culture and creating a new multiracial and multicultural heritage. |
Read the World Vision article on Ways to empower woman: Simple but visible
Girls’ education is a strategic development priority. Better educated women tend to be healthier, participate more in the formal labor market, earn higher incomes, have fewer children, marry at a later age, and enable better health care and education for their children, should they choose to become mothers. All these factors combined can help lift households, communities, and nations out of poverty. Read World Bank report on girl’s education.
Across the world calls to protect the planet are growing louder, yet standing up against the deleterious effects of mining, logging and agribusiness continues to be fatal. According to the Guardian report 164 environmental activists were killed in 2017 while protecting their homes. Read Guardian Report on the murder of the environmental activists.
Surprisingly, Rawanda with 62% of the female parliamentarians hold the record of the highest female parliamentarian in the world in 2018. One of the prime reasons behind this is absence of the male leaders due to the civil conflict in 1990s. Other countries with high proportion of female in the parliament is Bolivia, Cuba, Iceland, Nicaragua and Sweden. On the other hand, Yemen, Qatar, Vanuatu do not have any female representation in the parliament. Read World Economic Forum report of Female parliamentarian.
Dozens of gold miners have invaded a remote indigenous reserve in the Brazilian Amazon where a local leader was stabbed to death. Read Guardian article on how Amazon gold miners are violating the rights of the indigenous people.
Read the stories of the Ogoni people of the Nigar delta and they suffer death threats and targeted assassinations when campaign against the environmental degradation of the land and waters of their homeland. Read how the Petroleum giant Shell and the oil spills have devastated the entire area.
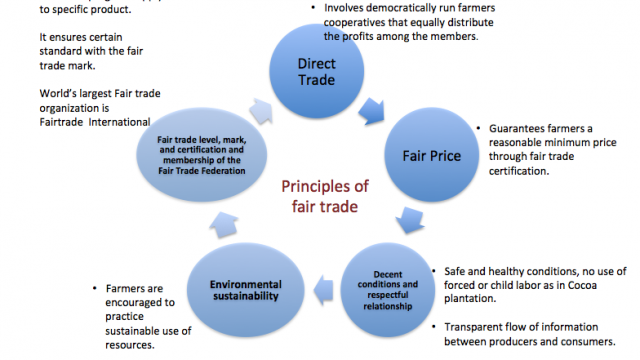
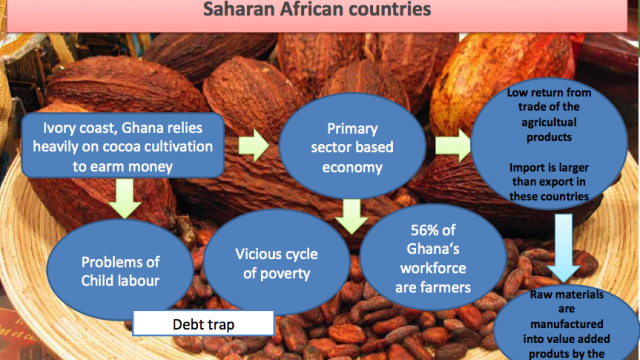
Alternative Trading Network: Fairtrade
References
- Chambers, R. (1997) Whose Reality Counts? Putting the First Last. London: ITDG.
- Chambers, R. (2004) Ideas for Development. IDS Working Paper 238. Sussex: IDS
- Kanbur, R. (2006) What’s Social Policy got to do with Economic Growth? Available at http://www. arts.cornell.edu/poverty/kanbur/ (accessed 1 August 2005).
- Thomas, A. (2004) The Study of Development. Paper prepared for DSA Annual Conference, 6 November, Church House, London.
- Reflections on Economic Development: The Selected Essays of Michael P. Todaro (Edward Elgar, 1995)
- http://www.worldbank.org/depweb/english/beyond/beyondco/beg_01.pdf
- https://www.nytimes.com/books/first/s/sen-development.html
- http://www.cmi.no/publications/file/953-a-balanced-view-of-development-as-freedom.
Data Sources
- Shaohua Chen and Martin Ravallion, The developing world is poorer than we thought, but no less successful in the fight against poverty, World Bank, August 2008.
- World Bank Key Development Data & Statistics. World Bank, accessed March 3, 2008
- Luisa Kroll and Allison Fass, The World’s Richest People, Forbes, March 3, 2007
- http://data.unicef.org/child-mortality/under-five
- http://www.globalissues.org/article/715/today-21000-children-died-around-the-world
- http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2013_en_summary.pdf
- http://www.worldbank.org/content/dam/Worldbank/document/Poverty%20documents/inequality-in-focus-october2013-v12.pd
- http://live.worldbank.org/building-shared-prosperity-unequal-world