The space station orbits the Earth in about every 90 minutes. That means in 24 hour, the space station orbits the Earth approximately _? times 🙂
A Better World Through Education
Think Bigger, Think Different, Think Greener
IBDP Geography Syllabus
The aims of the Geography syllabus SL and HL are to enable students to:
Develop an understanding of the dynamic interrelationships between people, places, spaces and the environment at different scales
Outline of The New Geography Syllabus 2019
| Diploma Programme geography SL and HL curriculum (first teaching September 2017) | SL teaching hours | SL assessment (first assessment May 2019) | HL teaching hours | HL assessment (first assessment May 2019) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part one | Geographic themes — seven options Two options are studied at SL, and three at HL Freshwater—drainage basins Oceans and coastal margins Extreme environments Geophysical hazards Leisure, tourism and sport Food and health Urban environments | 60 hours | Paper 1 SL weight 35% 45 minutes per option question Total 1 hour 30 minutes Each option has a structured question and one extended answer question from a choice of two. 20 (10 + 10) marks per option Total 40 marks | 90 hours | Paper 1 HL weight 35% 45 minutes per option question Total 2 hours 15 minutes Each option has a structured question and one extended answer question from a choice of two. 20 (10 + 10) marks per option Total 60 marks |
| Part two | SL and HL core Geographic perspectives —global change Population distributio n—changing population Global climate —vulnerability and resilience Global resource consumption and security | 70 hours | Paper 2 SL weight 40% Total 1 hour 15 minutes Paper 2 Section A Three structured questions, based on each SL/HL core unit 30 marks Paper 2 Section B Infographic or visual stimulus, with structured questions 10 marks Paper 2 Section C One extended answer question from a choice of two 10 marks Total 50 marks | 70 hours | Paper 2 HL weight 25% Total 1 hour 15 minutes Paper 2 Section A Three structured questions, based on each SL/HL core unit 30 marks Paper 2 Section B Infographic or visual stimulus, with structured questions 10 marks Paper 2 Section C One extended answer question from a choice of two 10 marks Total 50 marks |
| Part two HL core extension | HL only Geographic perspectives —global interactions Power, places and networks Human development and diversity Global risks and resilience | 60 hours | Paper 3 HL weight 20% Total 1 hour Choice of three extended answer questions, with two parts, based on each HL core unit 28 marks Part A—12 marks Part B—16 marks |
||
| Total examination time | 2 hours 45 minutes | 4 hours 30 minutes | |||
| Internal assessment | SL and HL Fieldwork Fieldwork, leading to one written report based on a fieldwork question, information collection and analysis with evaluation | 20 hours | Internal assessment SL weight 25% Fieldwork question to be based on any suitable topic from the syllabus Total 25 marks | 20 hours | Internal assessment HL weight 20% Fieldwork question to be based on any suitable topic from the syllabus Total 25 marks |
| Total teaching hours | 150 hours | 240 hours |
Click here to download IBDP 2019 Geography Syllabus and Subject Guide
IB Learner Profile and Rules and regulations of the Lesson
There are four assessment objectives (AOs) for the SL and HL Diploma Programme geography course
1. Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of specified content
- Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the core theme—patterns and change
- Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of two optional themes at SL and three optional themes at HL
- At HL only, demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the HL extension—global interactions
- In internal assessment, demonstrate knowledge and understanding of a specific geographic research topic
2. Demonstrate application and analysis of knowledge and understanding
- Apply and analyse geographic concepts and theories
- Identify and interpret geographic patterns and processes in unfamiliar information, data and cartographic material
- Demonstrate the extent to which theories and concepts are recognized and understood in particular contexts
3. Demonstrate synthesis and evaluation
- Examine and evaluate geographic concepts, theories and perceptions
- Use geographic concepts and examples to formulate and present an argument
- Evaluate materials using methodology appropriate for geographic fieldwork
- At HL only, demonstrate synthesis and evaluation of the HL extension–global interactions
4. Select, use and apply a variety of appropriate skills and techniques
- Select, use and apply the prescribed geographic skills in appropriate contexts
- Produce well‑structured written material, using appropriate terminology
- Select, use and apply techniques and skills appropriate to a geographic research question
Further guidance on IB approaches
Use of case studies and examples
Case studies and examples must be used where appropriate to illustrate content.
A case study is a detailed, located example for discussion or a discursive approach. Ideally, case studies
selected should be recent; that is, they should have occurred within the student’s lifetime and should not
be historical. The use of historical case studies could lead to students losing marks. For example, using the
destruction of Pompeii as an example of volcanic destruction is not recommended.
Geographic models
Students can study models to illustrate concepts relevant to particular topics but examination questions will
not require students to have prior knowledge of any specific model.
Use of maps and diagrams
Students are expected to include well‑drawn, large, relevant maps, sketches, tables and diagrams as often
as applicable. Only metric maps will be used for examinations.
Annotated maps
Examination questions frequently refer to “annotated maps”. Annotating maps requires students to include
comments on the map itself and to place these comments in the relevant locations. Comments must not be
written separately below the map.
Use of calculators
Calculators are not allowed in IB geography examinations.
Links:
Luma Labs – https://lumalabs.ai/
Google Earth Studio – https://earth.google.com/studio/
Luma Labs Genie – https://lumalabs.ai/discord
Perplexity – https://www.perplexity.ai/
SciSpace – https://typeset.io/
Google SGE – https://labs.google/
MusicGen (WaveFormer) – https://waveformer.replicate.dev/
MusicGen (HuggingFace) – https://huggingface.co/spaces/faceboo…
textfx – https://textfx.withgoogle.com/
LeiaPix – https://convert.leiapix.com/
Insta3D – https://huggingface.co/spaces/ilumine…
Animated Drawings – https://sketch.metademolab.com/
CapCut – https://www.capcut.com/
Replicate – https://replicate.com/
Upscayl – https://www.upscayl.org/
Illusion Diffusion – https://huggingface.co/spaces/AP123/I…
Ideogram – https://ideogram.ai/
Dalle 3 – https://www.bing.com/create
Google SGE – https://labs.google/
Playground AI – https://playgroundai.com/


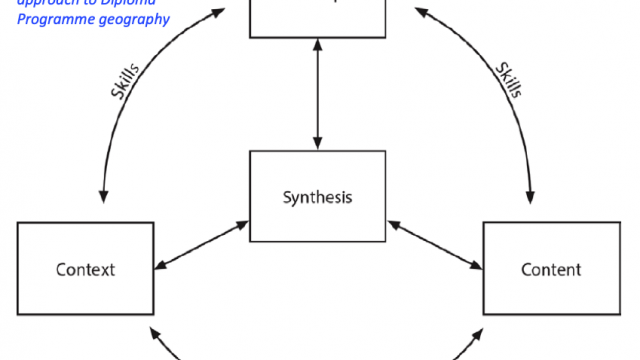

Develop a critical awareness and consider complexity thinking in the context of the nexus of geographic issues, including:
Acquiring an in-depth understanding of how geographic issues, or wicked problems, have been shaped by powerful human and physical processes.
Synthesizing diverse geographic knowledge in order to form viewpoints about how these issues could be resolved.
Understand and evaluate the need for planning and sustainable development through the management of resources at varying scales.
There are four assessment objectives (AOs) for the SL and HL Diploma Programme geography course:
Click here to know more about the structure of the New Geography Courses from 2019 onwards from the IBO official link