Powerful organization and global groups
G6 to G8 to G7
The Group of Eight Countries, or G8, was the name of a political forum that existed from 1997 until 2014. In 2014, it became the Group of 7, or G7. The forum was first started in 1975 as the Group of Six, or G6. The original countries that were members of this group were: France, Germany Italy Japan, United Kingdom and United States. In 1976, Canada was added to make it G7. Russia was added to the forum in 1997, but was suspended in 2014. Three years later, Russia announced that it would permanently withdraw from the forum. Today, the forum is known as G7. These seven nations have about 58% of the world’s total wealth represented as the total GDP of these nations.
BRICS
BRIC or Big Four is an acronym originally used to represent four countries that have similar economic development includes Brazil, Russia, India, China, began informally in 2006. The first official summit held in 2009 in Russia. At present, BRICS is the group composed by the five major emerging countries – Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa -, which together represent about 42% of the population, 23% of GDP, 30% of the territory and 18% of the global trade. Goldman Sachs economist, Jim O’Neill first used the acronym in 2001. Undoubtedly, the two most notable achievements of the BRICS have been the institutionalization of the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingency Reserve Arrangement. So far, the NDB has approved more than 8 billion-dollars in infrastructure and renewable energy financing projects in the BRICS countries. The CRA is operational and is an important financial stability mechanism for countries affected by crises in their balance of payments.
World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
The Main difference between IMF and the World Bank is in their proposes and operation. The IMF oversees the world’s monetary system’s stability, while the World Bank’s goal is to reduce poverty by offering assistance to middle-income and low-income countries. Both organizations are based in were established as part of the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1945, after the Second World War. IMF monitors member countries’ economic health and lends money to countries with balance of payments difficulties. However, the borrowing country must implement fiscal initiatives (tax and other economic measures) suggested by the IMF. On the other hand, World Bank provides support and aid for long-term economic development.
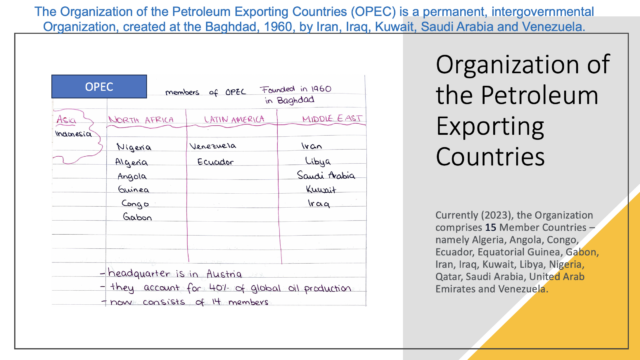
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization and a Cartel consisting of 14 major oil-exporting countries. It was founded in 1960 to coordinate the petroleum policies of its members and to provide the member states with technical and economic support. The OPEC member countries hold 75% of the crude oil reserve in 2019 and therefore exercise a great command over the crude oil price and supply in the global market.
OPEC members:
Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela (the five foundering members), UAE, Libya, Algeria, Nigeria, Gabon, Angola, Republic of Congo, Ecuador.
Recent challenges: The arrival of fracking technology in USA has reduced OPEC’s ability to control the world market, as many unconventional sources of crude oil are now accessible.
What is Fracking: It a slang that indicates the process of hydraulic fracturing that involves injecting specialized fluid into the cracks to create larger fissures that allow more oil and gas to flow out of the formations. It allows the extraction of oil and natural gas from low permeability sites where traditional extraction technology will not work efficiently. Therefore, drilling is now possible even from previously difficult-to-reach sources of oil and gas.
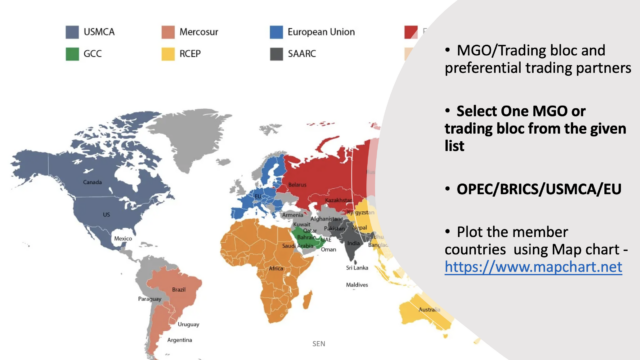
Multi-Governmental Organizations (MGOs)
The emergence of large trading bloc and Multi-governmental organization(MGOs) in recent years is part of the wider process of globalization. In some ways globalization can be viewed as a natural development from large trading blocs into a unified world market. At the simplest level, free trade associations have been set up between countries, such as Mercosur in South America, NAFTA in North America. On the other extreme trading associations may tend towards political integration and economic bullying, for example, in the European Union.
Impacts of Globalization
| Global Impacts | 1. Enhancement of world trade and growing power of TNCs and large brands. 2. Increasing interdependence and complexity of the global economy. FDI, outsourcing, role of the trading bloc such as EU, mass scale production are gaining more importance. 3. Cultural diffusion through labour movement, international tourism and migration playing a great role in the development of a hybrid global culture. 4. World is becoming a 'Global village' through high end connectivity and diffusion of internet technology. 4. Development of the civil society to safe guard interest such as Greenpeace. 5. Emergence of increasing number of NICs 6. Increasing cultural diversity within a country. |
|---|---|
| National level | 1. Increasing transboundary pollution for example Fly-tipping (illegal deposit or dumping of waste). 2. International tourism as rise of mass tourism. 3. Concern about loss of sovereignty (autonomous decision making power of a country). 4. Growth of anti-globalization movement as an overreaction to loss of jobs to international labour and increasing cultural diversity diluting national identity. 5. Repatriation of TNCs profit (not paying taxes to the local authority). 6. Rise of Alpha cities as global hubs. |
| Local | 1. Unemployment, uncertainty and loss of jobs due to the operation of the large global TNCs. Small local businesses find it difficult to compete with the large TNCs. 2.Rise of multicultural communities and cuisine. 3. Development of ethnic villages within cities such as China town in many megacities. 4. Creation of consumer culture and acceptance of global brands such as McD, Apple, Nike etc. 5. More connectedness through global social media such as facebook, instagram etc. |
Fun Learning
Memory game on Globalization
Memory game2 on Globalization
Try out card game of globalization (HL-Revision)