Hydrological characteristics and processes which operate in rivers and drainage basins.
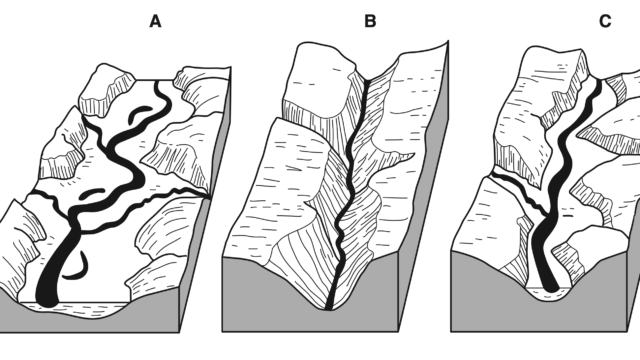
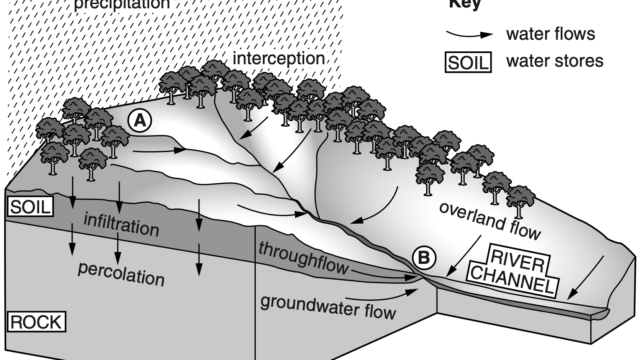
Drainage basin and water divide is the area drained by a main river and its tributaries, bounded by a watershed. Components of a drainage basin are main stream, tributaries and distributaries, wetland and estuary (mouth of a river which is tidal), the exit of the basin (where the waters join another water body such as a river, lake, sea, or ocean). Watershed or water divide is an imaginary line that separates adjacent drainage basins. It is generally a highland or ridge or plateau.
Your Tasks
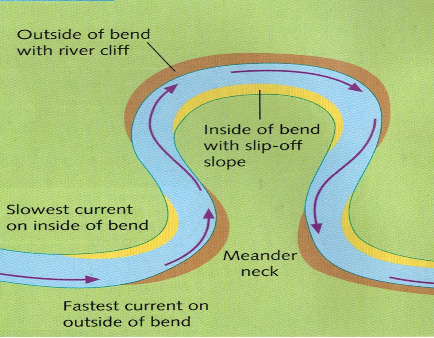
A. Draw annotated diagrams and explain.
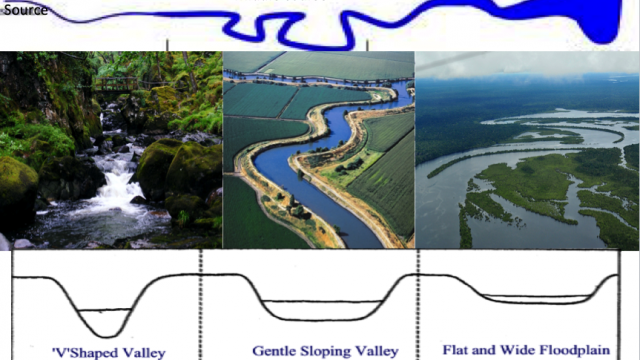
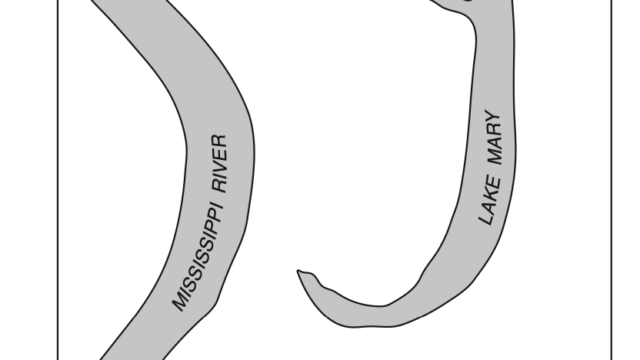
B. Look carefully the 2nd diagram carefully and ‘describe‘ the characteristics of lake Mary.
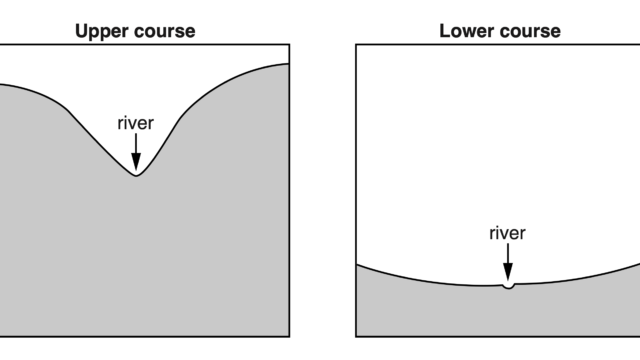
C. Notice the 4th diagram and using this diagram only, describe three differences between the cross section of the upper and lower course of a river. (try to use the given words: Wider, narrower, deeper, more V shaped etc.)
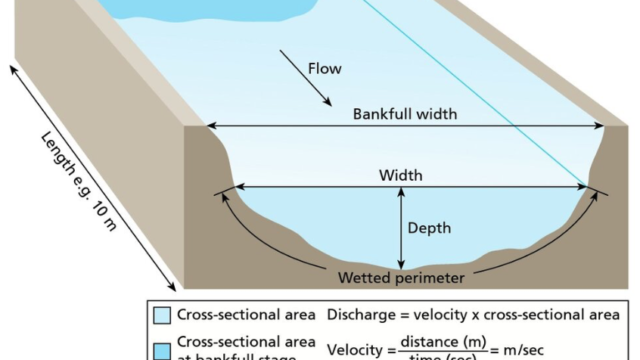
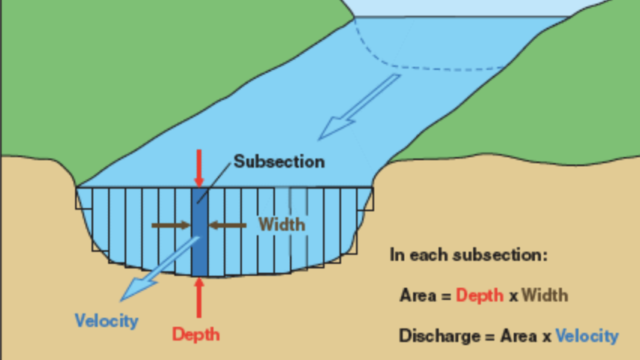
How to measure river velocity
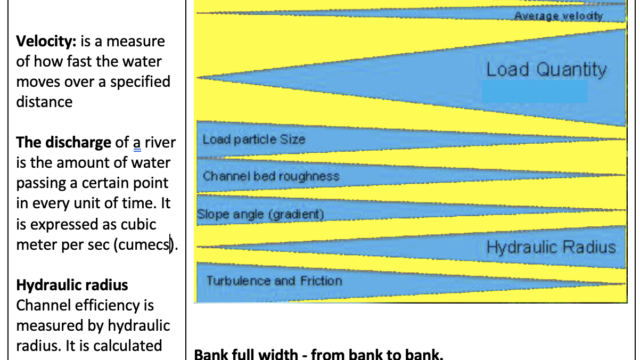
Velocity: is a measure of how fast the water moves over a specified distance. It refers to the rate of water movement, often measured in meters per second. Velocity can be measured through Float and flow method.
Float Method: Equipment and methodology
- Floating object, for example a tennis ball- float
- Ranging pole to mark the points of measurements
- Tape measure and stopwatch
The cheapest way that to measure velocity and discharge is the float method. One may need a 10m tape measure, a float (i.e., something that floats and is brightly colored, such as a bright tennis ball) and a stopwatch. At least two people are needed for this method. Mark the start and end points (10 meters is a good distance). Float should be thrown into the water slightly upstream of the start point. Using the stopwatch, time is recorded, how long it takes the float to move from the start point to the end point. Repeat this procedure at least three times to calculate the average and to minimize error.
Considerations and possible limitations
- The float used must be visible, durable and not to be affected by wind
- Be aware of possible user error meaning that the start or finish point is not very clear. Placing the object up-stream and having definite start and finish lines (through tape measures and placing of ranging pole) can help to minimize these errors
- This method only records surface velocity.
- Repeated measurement and taking averages can reduce the margin of error