| Optional Theme E. “Leisure, sport and tourism” | DEFINITIONS |
|---|---|
Tourism | Travel away from home for at least one night for the purpose of leisure. Note that this definition excludes day‑trippers. There are many possible subdivisions of tourism. UNWTO definition of tourism: Tourism means to travel away and staying in place outside of the usual home environment at least for one night but for not more than one consecutive year mainly for the purpose of leisure and recreation but also to visit friends and relations, for business and other personal reasons. |
Leisure | Any freely chosen activity or experience that takes place in non‑work time. |
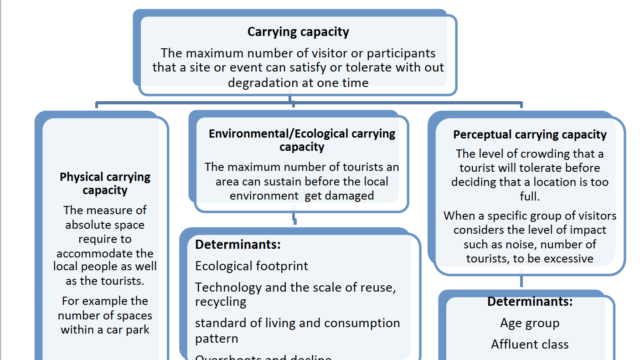
Carrying capacity of a touristic place | The maximum number of visitors/participants that a site/event can satisfy at one time. It is customary to distinguish between environmental carrying capacity (the maximum number before the local environment get damaged) and perceptual carrying capacity (the maximum number before a specific group of visitors considers the level of impact, such as noise, to be excessive). For example, young mountain bikers may be more crowd‑tolerant than elderly walkers. |
| Sustainable Development | Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs (Brundtland commission 1987). |
| Objectives of Sustainable tourism | Sustainable use of resources by meeting the needs of the present without harming the prospect of the future generation. Supporting and involving local communities and creation of local multiplier. Reduce-reuse-recycle (3R principles): reducing overconsumption and waste, recycling of tourists waste Use of efficient environmental alternatives (ecofriendly paper bag, biking rather than using vehicles for sightseeing) Maintaining biodiversity Research and training, providing better information Promoting respect for the natural, social and cultural environments Integrating tourism into planning for development |
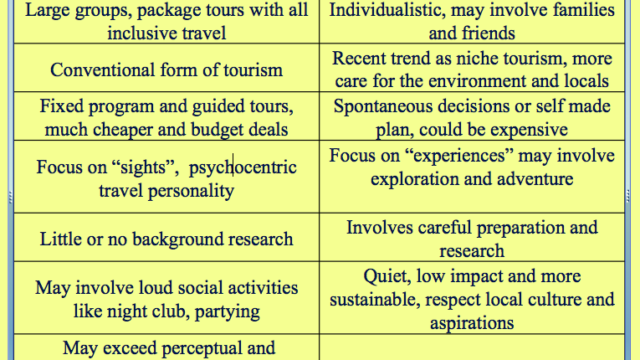
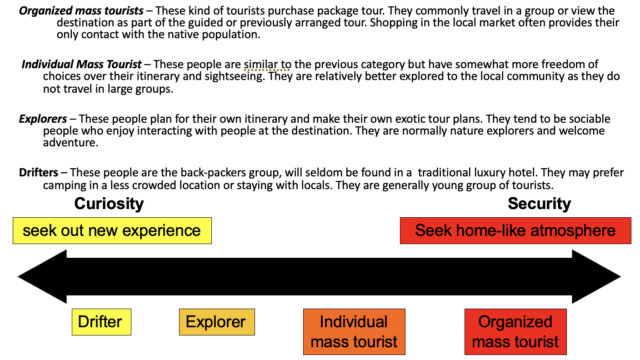
Mass Tourism | Mass tourism involves large number of tourists flocking into certain popular destinations. This kinds of tourism are generally operated by large touristic operators though package tours and are relatively cheaper but may adversely affect the local environment and community. |
| Threshold population of a service | The minimum number of people/customers necessary to support an economic activity (a facility or service) to run at a profitable scale. |
Alternative or Niche tourism | it is a kind of special interest tourism involving small number of tourists to relatively less explored places involving respect and care for the local community and greater concern of nature. It may also involve explorative touristic activities generally not suitable to a large number of tourists. |
Primary tourist/recreational resources | The pre‑existing attractions for tourism or recreation (that is, those not built specifically for the purpose), including climate, scenery, wildlife, indigenous people, cultural and heritage sites. These are distinguished from secondary tourist/recreational resources, which include accommodation, catering, entertainment and shopping. |
Recreation | A leisure‑time activity undertaken voluntarily and for enjoyment. It includes individual pursuits, organized outings and events, and non‑paid (non‑professional) sports. |
Resort | A settlement where the primary function is tourism. This includes a hotel complex. |
| Global Middle Class (New Global Middle Class and Fragile middle class) | People with discretionary or disposable income (income left after meeting the basic needs of the life to spend for non-essential consumer goods and commodities such as car or services such as tourism, private health care etc.) are the middle class. According to the recent World Bank classification people earning more than US$10000 annually can be considered as the NGMC. 90% of the world population at present lives above the Extreme Poverty line (living on less than US$1.90per day). However, nearly 2 billion people belongs to the poorer group of middle class with earning or spending capability between US$ 2 and US$10 per day. This group might easily slide back to extreme poverty with any economic crisis situation. These group of people are known as Fragile Middle Class. |
Sport | A physical activity involving a set of rules or customs. The activity may be competitive. |
| Classification of Tourism related to distance and borde | Domestic tourism (inbound tourism) embraces those, travelling within their own country. International tourism (outbound tourism) comprises those, who travel to a country other than that in which they normally live. Long-haul tourism; taken to be journeys of over 3000 kilometres Short-haul tourism; comprises journeys below that distance |
| Eco-tourism Vs Sustainable tourism | These are two different concepts with different underlying principles. An ecotourism project doesn’t, by definition, have to be sustainable but it is. And sustainable tourism doesn’t have to involve the environment but it does. Eco-tourism predominantly focuses on the preservation of the quality of the natural environment and the culture/traditions of the local communities. In most cases it turns into a form of sustainable tourism—tourism that conserves primary touristic resources and supports the livelihoods and culture of local people so that the touristic resources can be experienced for generations. Longevity of tourism is the prime focus of the sustainable tourism. |
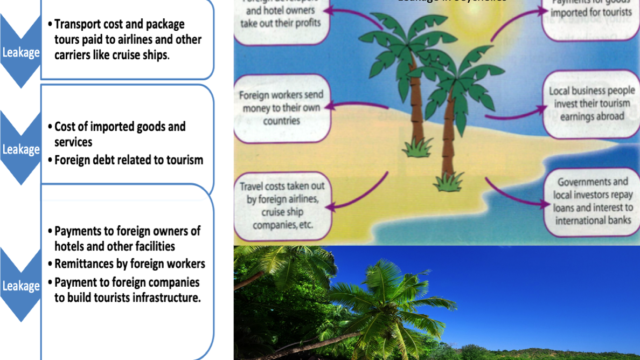
Leakage (Negative) | Economic loss of tourists money, by tourists using companies not owned by the host country and spending money outside the host country (for example on a cruise ship) It implies that the tourists money moving out of the host economy due to several reasons, leaving not much opportunity left for the local people to profit from tourism |
Multiplier effect (Positive) | Multiplier effect of tourism means that income gained by local people is circulated through the economy creating more wealth in turn. Explanation for 4 marks question: When an initial amount of spending usually by the government leads to an increased spending by tourists, resulting in an increase in national income much greater than the initial amount spent. It means Income gained by local people is circulated through the economy. Tourism not only creates jobs in the tertiary sector, it also encourages growth in the primary and secondary sectors related to tourism. |
Trickle down effect of tourism (positive) | Trickle down effect starts in the core region (major touristic area) and spreads to the whole of the system particularly to periphery. It is extremely important where tourism is considered as an effective development strategy, such as in many SIDs. |
Food miles | A measure of the distance that food travels from its source to the consumer. This can be given either in units of actual distance or of energy consumed during transport. |
Transnational corporation (TNCs) | A firm that owns or controls productive operations in more than one country through foreign direct investment. |
| Heritage tourism | tourism based on a historic legacy (landscape feature, historic building or event) as its major attraction. |
| Enclave tourism | Local businesses often see their chances to earn income from tourists severely reduced by the creation of "all-inclusive" vacation packages. When tourists remain for their entire stay at the same cruise ship or resort, which provides everything they need and where they will make all their expenditures, not much opportunity is left for local people to profit from tourism- this is known as enclave tourism (a form of leakage). |
| Leisure hierarchy | Leisure hierarchy denotes high and low order leisure activities and services. Services or places rank higher in the leisure hierarchy has less frequency means they are less in numbers. Higher order leisure hierarchy such as Lego land, Multiplex shopping complex etc. are of bigger sizes and have greater spacing between them due to the sharing of threshold population. Services or places rank higher in the leisure hierarchy has higher range with vast catchment areas. Services or places rank higher in the leisure hierarchy has more cost of installation/ or they are normally high priced facilities. |
| Demographic factors affecting participation in sports | Gender (male/female), Family life cycle and age, Place of residence (rural or urban residents) |
According to UNWTO REPORT, International Tourism to Reach Pre-Pandemic Levels in 2024
Approaches to understand tourism and it‘s role
Tourism means travel away from home mainly for the purpose of leisure for at least one night but not more than one consecutive year. Day tripping is not regarded as tourism (World Tourism Organization, UNWTO).
Benefits of tourism
Tourism can be viewed as a commercialized hospitality, travel and leisure industry – an industry to earn foreign exchange.
Tourism as a means to get knowledge, sharing cultural values and respect to humanity.
Promoting conservation – eco-tourism and sustainable tourism (alternative tourism)
Tourism as a strategy for development generating multiplier effect.
Multiplier Effect: When an initial amount of spending usually by the government leads to increased spending by the tourists and results in an increased national income greater than the initial amount spent. Tourism can also be transformed as the modern variety of traditional pilgrimage, adventure and exploration.
Both in numbers and spending, the number one source of international tourists is China. In the league tables of the continents, Europe holds the number one spot as the most visited continents with more than 500 million visitors per year.
UNWTO forecasted a growth of 4% in international tourist arrivals worldwide in 2021. Read the UNWTO-World Tourism Barometer, 2022
Click here to review the most visited countries of the world according to the worldatlus.com
Find out Forbes report on the world’s fastest growing touristic destinations.
Tourism is one of the world’s largest economic sector that creates jobs, drives exports, and generates prosperity across the world. Tourism is accounted for 10.4% of global GDP and 319 million jobs, or 10% of total employment in 2018. Over the decades, tourism has experienced continued growth excluding the recent corona pandemic period.
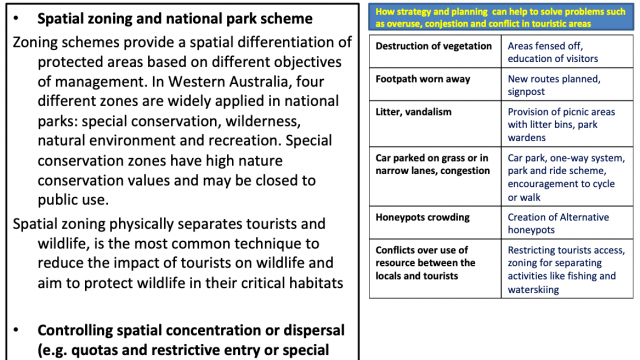
Review: Why should mass tourism be avoided? Mention some of the techniques to regulate mass tourism.
Factors affecting travel decision: https://youtu.be/vWPFhdz3G7E
Both in numbers and spending, the number one source of international tourists is China. In the league tables of the continents, Europe holds the number one spot as the most visited continents with more than 500 million visitors per year (pure pandemic level).
Suggest reasons why there is more leisure time in some countries than others?
Establish a link between economic development and participation in leisure activities?
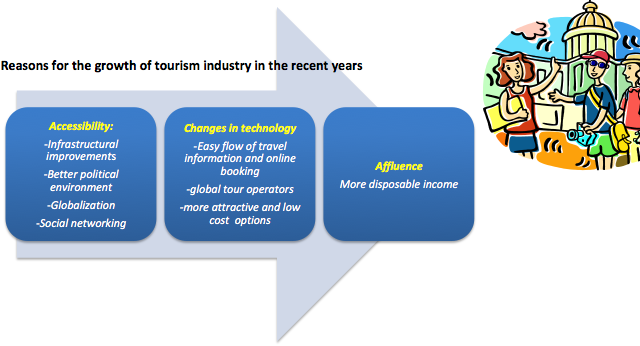
Reasons for the growth and changing purposes of global leisure and tourism industry
Economic reasons- Affluence and greater accessibility
- Rising disposable income of the middle class . Now people have that extra money to spend.
- Decreasing cost and travel time (eg. Budget airlines) and travel rewards (air miles, bonus points etc)
- Increase in number of options and widening range of destinations. Paid holidays – People no longer need to save up their income through unpaid holidays.
Social and technological reasons
- Increase in creative and high skilled jobs, increase in paid leave as part of employee welbeing efforts of the companies. The number of hours in the working week have decreased. This means people have more time for leisure activities.
- Increasing desire to experience different cultures and landscape
- Increasing media coverage, greater accessibility and ease of travel
- Increase in international migration, diffusion of culture and social networking (people have relatives and friends living abroad)
Political reasons
- Many government has invested heavily to encourage tourism (as a development strategy)
- Government initiatives for major international events like Olympic and World Cup also attract huge amount of tourists.
- Better political link and coperation. For example: President Obama’s historic trip to Cuba on 20thMarch 2016 and meeting with country’s leader President Raúl Castro. It is the first presidential trip to Havana in nearly 90 years (since Calvin Coolidge in 1928). The number of Americans visiting Cuba increased by 77 percent in 2015, a figure that’s likely to increase further as US airlines open up direct flights to Cuba. Under the present Trump administration’s effort to bring about the end of Cuba’s repressive government by squeezing the island’s economy promises only more suffering for Cuban citizens and decease in tourist flow.
Physical and human factors: Primary and Secondary touristic resources
Primary touristic resources are the physical factors that shape places into sites of leisure and tourism:
- These are attractions that pre-date tourism (not built for the purpose of tourism). Primary resources include the climate and other physical conditions such as scenery, wildlife, history and heritage.
Secondary touristic resources are those human factors that shape places into sites of leisure and tourism:
- The extra facilities that are built to accommodate the tourists (hotels, restaurants, water parks, shopping and Cineplex etc.)
Read and understand: What are the different types/segments of niche tourism?
Identify the major primary and secondary touristic resources in Venice
Movie location Tourism:
Utah, Moab and its fabulous red rock formations, canyons and Monument Valley: 127 Hours is the harrowing true story of Aron Ralston, who became trapped in a canyon with his arm pinned under a boulder. Facing certain death, he decides to do the unthinkable, and cut off part of his own arm in order to escape.
Click here to read about the most famous movie locations that draw thousands of tourists every year.
The ‘magical Greek island of Kalokairi’ where most of Mamma Mia! was filmed. Dubai skyline full of sleek and shiny skyscrapers served as a perfect vertical alien world of Star Trek. Zhangjiajie National Forest Park in Hunan Province of China, known for its unbelievable sandstone quartz pillars was the location of the award winning movie Avatar.
Avatar, a film by James Cameron, that was nominated for a total of 9 Academy Awards in 2010, took inspiration for its mountain scenes from the peaks of Hunan province. This beautiful place now experiencing touristic boom as a destination of movie location tourism. The world’s highest glass-bottomed bridge is also located here. Tianmen mountain, which boasts the world’s longest cable car ride and spectacular views are all part of this UNESCO-listed World Heritage Site. Read more to know how this movie location is able to generate tourism boost in the Hunan province of China.
Tourism in Zhangjiajie has been developing rapidly. Rapid tourism growth bringing about an increase of household incomes and government revenues through multiplier effects, and has become a dominant driver for local economic growth. The Surrounding villages were able to to move out of poverty due to this tourism-led growth. Click here to read how Huangshi Village, located in the scenic area of Zhangjiajie, has become one of the top 5 highlight travels in China. Economic impact of tourism in and around China’s Zhangjiajie City is mainly propelled by the domestic tourists after the Avatar shoot. Click here to read how Zhangjiajie has been advertised as the movie location by the city mayor.
Case Study: Urban Tourism Hotspot, Las Vegas, USA
Primary touristic resources in Las Vegas:
The largest city in Nevada, Las Vegas lies in the desert, surrounded by baron hills.
Las Vegas is a great place to visit year-round; its cooler winter temperatures are pleasant for sightseeing, and in summer, when the temperature can rise 40 degree C, the outdoor pools and fountains become important part of the daytime activities.
Grand Canyon over river Colorado
Las Vegas has a number of companies providing helicopter tours that take visitors over Las Vegas and the Strip, or as far away as the Grand Canyon, America’s most impressive and famous natural attractions.
Las Vegas Natural History Museum can be considered as a heritage site.
Secondary Tourism Resources
The extra facilities that are built to accommodate the tourists (hotels, restaurants, water parks, shopping and Cineplex etc.)
Example: Las Vegas is the largest gambling destination in the world. In 2015, it attracted over 42 million visitors and earned gambling revenue of over 9 billion US dollar.
Las Vegas Boulevard strip and Fremont Street Experience– The Strip is particularly impressive at night, when the city is illuminated and light up the sky in a ray of different colors fantastic music and visual show takes place overhead.
The huge resort hotels lining the famous “Strip,” with their sparkling lights, fountains, and recreated glamorous sites, offer a fun and exciting retreat from the desert landscape.
Read Articles related to the touristic attractions in the city of Las Vegas
Famous Theme hotels in Las Vegas: Las Vegas has 5 of the world’s 10 biggest hotels
- Paris Las Vegas Hotel with its ½ scale replica of the Eiffel Tower outside.
- The Mirage hotel is a tropical paradise filled with colorful flowers and plants and home to an incredible erupting volcano show at night.
- Caesars Palace has played host to celebrities and high-rollers since its opening in 1966. It is known for its opulent Garden-of-the Gods, a 4 -acre pool area with roman statues, marble columns.
- The Excalibur is one of the grandest hotels in Las Vegas and is considered one of the best in the city. This is already an amazing feat considering that the medieval-themed hotel
43% of the total work force in Las Vegas was involved in the tourism sector in 2015. The average room rent per night in Las Vegas was 115 US dollar in 2015.
Reasons behind the development of the tourism industry in Las Vegas, USA?
- The state’s liberal gambling regulations
- Electricity generated from the bounder dam
- The attractive hot dry climate and desert landscape
- Good accessibility- regular air services from all large cities of USA, It is only 420 km from Los Angeles and is connected by highway 15.
Challenges to Las Vegas touristic development
- Higher Mass Transit travel times. Road congestion is a major problem. Driving in Las Vegas is very expensive compared to most cities.
- Being a major gambling location, Families with children generally do not prefer Lag Vegas as their touristic destination.
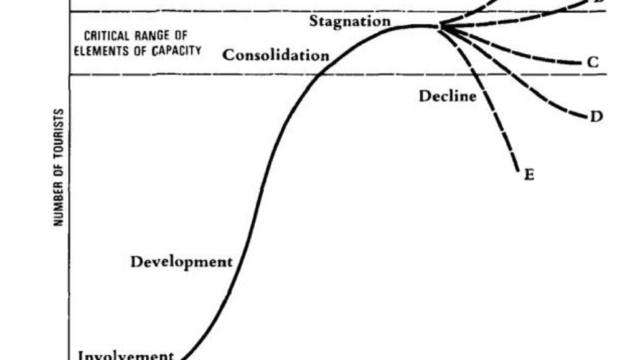
- Las Vegas has become one of the fastest growing cities of America, however, being a desert city, it has limited physical carrying capacity.
- Perceptual carrying capacity diminishes during the peak season due to overcrowding.
- Nevada is one of the unhealthiest states in the country. It’s also the suicide capital of America. All these have promoted the growth of urban crime, proliferation of the drug gangs and fraudulent and sex tourism.
Article Review:
Find out the challenges to growth of tourism in the urban touristic hotspot of Dubai
Refer to the Arcgis journal (Esri) on Positive and negative effects of tourism in Dubai
Dubai’s environmental problem and decreasing environmental carrying capacity
Tourism as a development strategy
Small islands developing states (SIDS) and remote areas: Small island states heavily relied on tourism as a lever to economic development as limited land area and narrow resource base restrict manufacturing on large scale. Small Island Developing States (SIDS) forms a distinctive group which shares many characteristics and whose vulnerability and special situation has been recognized by the international community.
Why is tourism viewed as an effective development strategy?
1. Rising per capita income generates multiplier effect as income gained by the local people is circulated through the economy. It can set of the process of cumulative causation whereby one phase of investment can trigger subsequent phases of investment in other sectors.
2. On the other hand many small island nations and developing countries have few other resources that they can use to obtain foreign currency.
3. A major tourism development can act as a growth pole, stimulating the economy of the larger region. By providing employment in rural areas it can help to reduce rural-urban migration. Touristic node can act as a growth pole and subsequently, the entire region may undergo further expansion causing a spread effect or trickle down effect on the surrounding regions or peripheral areas.
Note: Trickle down effect starts in the core region and spreads to the whole of the system particularly to periphery.
4. It can support many jobs in the informal sector, which plays a major role in the economy of the many developing countries.
5. Reinforces preservation of heritage and tradition.
It can lead to greater understanding and cultural exchange between people of different cultures.
Generates appreciation of historical legacy.
Family ties may be strengthened by visit to relatives.
Tourism can be viewed as a mean to get knowledge, sharing cultural values, promoting conservation and respect to humanity by promoting eco-tourism and sustainable tourism (alternative or Niche tourism)
| Problems and tourism Management | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Environmental challenges to touristic expansion | Increased water consumption, increased traffic and associated pollution (water, noise, aesthetic), loss of habitat and biodiversity, increased waste produced requiring disposal, CO2 emissions and higher carbon footprint (especially in case of the long-haul flights), consumption of local natural resources, price inflation. |
| Enclave tourism | Local businesses often see their chances to earn income from tourists severely reduced by the creation of "all-inclusive" vacation packages. When tourists remain for their entire stay at the same cruise ship or resort, which provides everything they need and where they will make all their expenditures, not much opportunity is left for local people to profit from tourism. |
| Critical issues in Tourism development in Seychelles | Seychelles has met all its UN developmental goals with more than 95% of the population having access to drinking water and electricity, but it is evident that existing infrastructure will not be adequate to meet present trends. Food security will remain an issue in view of the country’s dependence on imported food, and increased pressure to further convert existing agricultural land. There is an increasing trend towards consumption that creates ever larger ecological footprints, including increasing generation of wastes. Seychelles’ unique and diverse biodiversity is under threat primarily from intense tourism development pressure, environmental degradation and pollution. Impacts of climate change are likely to become more evident. |
Article Review :
Leisure, Tourism and Sports Flip Board Magazine
Ecotourism and Sustainable tourism
- Tourism that focuses on natural environment and local community
- Low-impact adventure tourism in a natural setting; sometimes called “green tourism.”
- Sustainable tourism focuses on conservation of primary tourist resources and supports the livelihood and culture of local people. It is organised in such a way that its level can be sustained in future with out creating irreparable environmental, social and economic damage to the receiving area.
- Ecotourism is a form of sustainable tourism. It is a specialized form of tourism where people experience relatively untouched natural environment (such as coral reefs, tropical rain forests and remote mountains) and ensure that their presence do not damage the environment
References:
https://www.napier.ac.uk/~/media/worktribe/output-209366/fullthesispdf.pdf
https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/travel-transport-and-logistics/our-insights/huanying-to-the-new-chinese-traveler