| Subject Specific Terms (related to migration) | Definitions | Extra Reference |
|---|---|---|
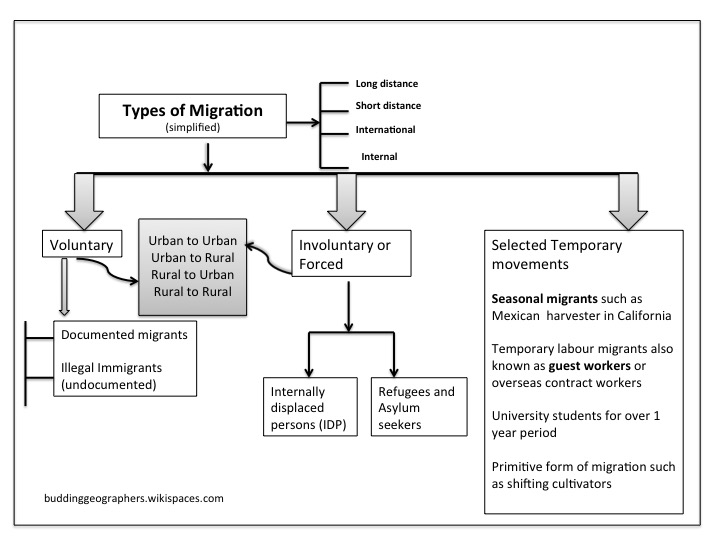
| Migration | The movement of people involving a change of residence. It can be internal displacement or international, voluntary or forced. It is usually for an extended period of time (more than a year) and does not include temporary circulation such as commuting or tourism. Migrations are broadly classified as Involuntary (forced) and Voluntary migration Long distance and Short distance migration International and Internal migration Most of the international organizations such as Amnesty International consider migrants to be people staying outside their country of origin, who are not asylum-seekers or refugees. | The number of international migrants globally in 2019: 272 million (3.5% of the world’s population) • 52 per cent of international migrants were male; 48 per cent were female. • 74 per cent of all international migrants were of working age (20–64 years). (Data Source: UN World Migration Report 2020) |
| Emigration | The process of leaving one country to take up permanent or semi-permanent residence in another. |  |
| Brain-drain | The emigration of a significant proportion of a country’s highly skilled, highly educated professional population, usually to other countries offering better economic and social opportunity. | |
| Remittances | Transfer of money or goods by foreign workers to their home country. | Read Case study: How Remittances to Afghanistan are lifelines: They are needed more than ever in a time of crisis . |
| Refugee | A person fleeing their home country in order to escape danger such as to escape war, persecution or natural disaster. According to international law, refugees have a right to international protection. Europe faced its worst refugee crisis since the Second World War in the last decade (2010-2020). | |
| Asylum seekers | People who seek refugee status in another country. Seeking asylum is a human right. This means everyone should be allowed to enter another country to seek asylum is seeking protection from persecution and serious human rights violations in another country, but hasn’t yet been legally recognized as a refugee. | |
| Illegal immigrants | People who enter another country without permission to remain there. | |
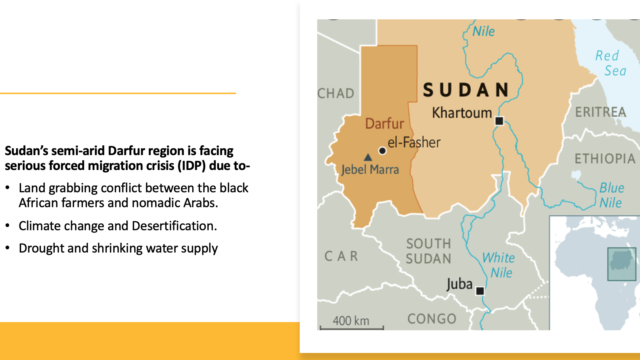
| Internally displaced people (IDPs) | Those involuntary migrants who have fled their homes but continue to live in their own country as they find shelter in another part of their country. Currently as per the UNHCR data , 71 million people have been forcibly displaced due to conflict, persecution or natural disasters in 2021. Check Amnesty International for more. |
Voluntary migration
Voluntary migration a free movement of migrants for an improved quality of life and personal freedom such as to find a job or to earn a better salary, better amenities such as hospitals, schools, mild climate specially on retirement or simply to be with family (marital dislocation) and relatives.
Can be based on some past legacy, for example: a significant proprotion of immigrants to UK has come from the former British colonies in the Indian subcontinent, Africa and Jamaica when Britain had a labour shortage after the Second World War. Trade and economic expansion associated to globalization led to free movement of skilled labour across boundaries, for example- IT employees from the Asian sub continent to USA and West European countries, migration of nurses from Philippines to UK etc.
Forced Migration (IDPs, refugees)
Forced migration occurs when the migrants have no personal choice but have been forced to leave their home country or regions in fear of persecution for reasons of religion, civil war or may be due to natural disaster.
Asylum seekers: people who seek refugee status in another country.
Forced migration may take place due to religious or political persecution, ethnic conflict, forced labour as slaves in the past (majority of the African slaves were brought to British North America between 1720 – 1780), lack of food due to famine, natural disaster and overpopulation. For example: Palestinian Arabs were forced to live in refugee camps following the creation of the state of Isreal in 1948. Over 3 million Afghan refugees have been forced to flee to neighbouring Pakistan and Iran as a result of 30 years of civil war. More that 2 miillion Iraqis have sought refuge in Jordon. More than 50% of Syria‘s population is currently displaced due to civil war and ethnic conflict. An estimated 9 million Syrians have fled their homes since the outbreak of civil war in 2011 to Egypt, Iraq, Jordan Turkey, Lebanon, Germany, Sweden and Austria (Amnesty International Sep. 2015)
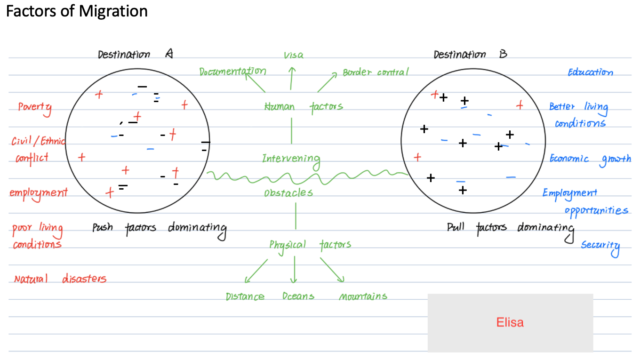
Game: Factors of migration
Accounts on migration and recent statistics
See People-on-the-move- Amnesty International
Syria’s refugee crisis in numbers
The UN Refugee Agency (UNHCR)
Impacts of rural to urban migration on the rural area
- Imbalance in age sex structure and male working class tends to move out.
- This may create social problems like no one to look after elderly.
- Underused services e.g. schools/shops may close down;
- People may need to ravel further to access services as many services will close down due to lack of threshold population.
- Positive aspect: Less pressure on utilities and services for example (water supply)