Global Interaction: Concept and definitions
| Terms | Definition /Explanation |
|---|---|
| Globalization | “The growing interdependence of countries worldwide through the increasing volume and variety of cross border transactions in goods and services and of international capital flows, and through the more rapid and widespread diffusion of technology” (source: IMF). It is a process that erodes national boundaries, integrates national economies, culture, technologies and governance, and produces complex relations of mutual interdependence |
| Globalization indices | The AT Kearney Foreign Policy index measures twelve variables, which are subdivided into four “baskets”: economic integration, personal contact, technological connectivity and political engagement. Nations are ranked according to a calculated globalization index. The KOF index measures three main dimensions of globalization: Economic, political and social, and nations are ranked accordingly. It is designed by the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology on a yearly basis. |
| Global Village: | The term global village was popularised by Marshall McLuhan, in his books The Gutenberg Galaxy: The Making of Typographic Man (1962). He pointed out the role of electronic media to create unified communities. He visualized the world as a global village, empowered by electric technology and the instantaneous movement of information |
| Global Hub | Well-connected places are called global hubs in network theory. London, New York city, Singapore, Shanghai, Hong Kong, Dubai, Tokyo, Mumbai, Frankfurt all are considered as global hub. Global hub includes Alpha ++, Alpha + and Alpha cities. Alpha ++ cities are most integrated with the global economy. Alpha cities are mostly large megacities with large frequency and density of interconnectedness. They are also considered as the primary nodes in the global economic network. Cities are ranked by the Globalization and World cities research Institute (GaWC) based on several economic, social and cultural factors. GaWC is the leading institute ranking world cities. The latest ranking has been done based on 2016 data |
| Grobalisation: (Neo-imperialism) | The imperialistic ambitions of nations (based on ideas of superiority and practices of dominance, and involving the extension of authority and control of one state or people over another) corporations and organisations to impose themselves on various geographic areas. |
| Cultural imperialism | The practice of promoting the culture/language of one nation in another. It is usually the case that the former is a large, economically or militarily powerful nation and the latter is a smaller, less affluent one. |
| Foreign direct investment (FDI) | Denotes a long-term investment where a firm based in one country (origin) establishes its presence in another country (host). It may refer to - 1. Investment in new facilities or production or services (Greenfield investment) 2. Acquiring and controlling significant percentage of the stocks of existing local companies (merger and acquisition in the long run) so that investor has control of the acquired assets (Brownfield investment) |
| MNE/MNCs/TNCs | A multinational enterprise is a company or firm that has established production or other operations in more than one country through foreign direct investment. According to World Investment Report, there are more than 82000 TNCs worldwide with more than 800000 foreign affiliates. Top 20 world largest corporations in 2017 are mostly American, Chinese, Japanese and French and German. (Core country domination) |
| McDonaldization (McD as the symbol of globalization) |
|
| Tariff (an anti globalization measure by the governments) | It is a tax on import as a result of which the domestic price of the product increases. It is assumed that if the price of the imported products raises then the level of domestic production of that commodity will increase. Tariff also generates revenue for a government. |
| Trade barriers (distorting free trade – slowing down globalization) | are government-induced restrictions on international trade. The barriers can take many forms, including tariffs and non-trade barriers. Non-tariff barriers to trade:
|
| Subsidy | A subsidy is a benefit given by the government to groups or individuals, usually in the form of a cash payment or a tax reduction. E.g. CAP subsidy in EU. CAP was launched in 1962 to achieve food security, rural development and to maintain the supply of affordable, safe and good quality food. It accounts for 40% of EU budget. |
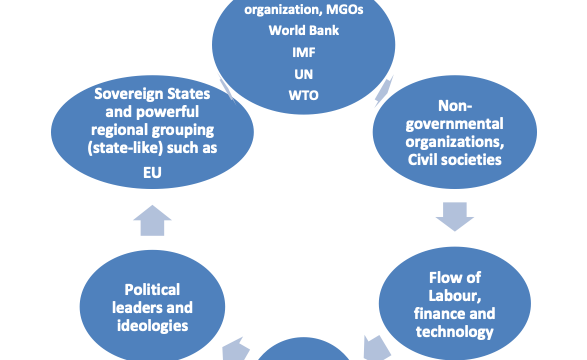
| Civil society | Any organization or movement that works in the area between the household, the private sector and the state to negotiate matters of public concern. Civil societies include non‑governmental organizations (NGOs), community groups, trade unions, academic institutions and faith‑based Organizations. (IB guide) Civil society is the aggregate of all associations, organization, movements and individual citizens independent from the state that manifest interests and will of citizens and aim to transform policies, standards or social structures through collective efforts at a national or international level. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) uses the term “civil society organization” to refer to the wide range of citizens’ associations that exists in virtually all countries to provide benefits, services, or political influence to specific groups within society. |
| Core and periphery | The concept of a developed core surrounded by an undeveloped periphery. The concept can be applied at various scales. |
| Food miles | A measure of the distance food travels from its source to the consumer. This can be expressed either in units of actual distance or of energy consumed during transport. |
| Glocalization | Emphasizes that the globalization of a product is more likely to succeed when the product or service is adapted specifically to each locality or culture in which it is marketed. The increasing presence of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide is an example of globalization, while changes made to the menus of the restaurant chain in an attempt to appeal to local tastes, are an example of glocalization. For example, McDonald’s in India serves Vegetable McNuggets (instead of chicken base) and Mutton based Maharaja Mac (instead of beef base Big Mac) as religious norms prohibit Hindus (80% of India’s popular are Hindus) to eat beef. This also caters to the needs of vegetarian consumers. |
| Outsourcing | The concept of taking internal company functions and paying an outside firm to handle them. Outsourcing is done to save money, improve quality or free company resources for other activities. |
| Trans-boundary pollution | Pollution event affecting more than one country. E.g. BP oil spill in Gulf of Mexico in 2010. It is the largest offshore oil spill in U.S. history. The Deep-water Horizon oil spill released 134 million gallons of oil into the Gulf of Mexico over a period of 87 days, fouling 1,300 miles of shoreline along five states (Ref: NOAA). It was a marine ecosystem disaster. |
| Homogenization of landscapes | Evolution of uniform urban landscapes; the effects of common commercial activity, structures, styles of construction and infrastructure. |
| Cultural traits | Traits in terms of language, customs, beliefs, dress, images, music, food and technology. |
| Time- space convergence – and the shirking world |
|
| Consumer culture | It is more than just a process of material transaction. It is a form of capitalism in which the economy is focused on the selling of consumer goods by creating artificial wants. The equation of personal happiness is now linked with certain types of consumptions and the purchase of material possessions. Mass media is used for the dissemination of the consumer culture, which is very important to the success of many TNCs/MNCs. .The mass media has been used very effectively to encourage consumers to want more than they need. The marketing industry uses all elements of the media to create a positive image of the products and services of the clients. It promotes the desire to keep up with one's peers, the belief that purchasing a new gadget or other piece of merchandise will improve quality of life, emphasis on shopping for leisure are all parts of consumer culture. |
| Brand | It denotes distinguishing name or symbol associated with the identity of a product or service. It is one of the most valuable assets of a company. Strong brands have the power to create considerable competitive advantage and can increase revenue by ensuring higher demand and market share. Increase profitability by producing in economic scale and by commanding brand prices. Reduces the cost and risk of introducing a new product due to a strong customer base. |
| Brand identity | It is the image and values associated with a brand. It may consist of features and attributes like brand logo, trading methods, performance, quality, service support. Brand identity is everything the company wants to create for its business. |
| Brand image | It implies the average consumer perceptions about the brand. |
| Brand franchise | McDonald’s is an example of a brand franchise. McDonald’s, the franchisor grant the right to sell its branded goods to someone wishing to set up their own business under McDonald’s franchise. McDonald’s owns and leases the site while the franchisee buys the equipment and the right to operate for 20 years. To maintain the uniformity of the operation, all franchisees must use standardized branding design layouts, branded menus, manufacturing methods, quality and administration systems. |
| Sovereignty | The absolute, supreme and ultimate dominion or authority of a political state expressed within its territory without the existence or influence of any other higher authority or power. Sovereign is embodied in the political institution od state. It denotes supreme authority within the territory and complete freedom from outside government |
Aspects of globalization
Economic globalization
- Rapid and huge increase in cross border economic activity
- Enabling financial and investment markets to operate internationally as a result of deregulation, improved communication and infrastructure.
- Increasing integration, linkage, diffusion and interdependence among the economies, particularly in cross border movement of goods, services and capital.
How:
- Growth of TNCs, ICT (information and communication technology services), online trade (Amazon, ebay), Portfolio investment and FDI
- Linkage between production chains,
- Comparative advantage in production
- Expansion of global market/ global consumer.
Social globalization
Social globalization involves expansion of global linkages, organization of social life on global scale, growth of global consciousness, and consolidation of world society.
How
- International immigration created extensive family network
- Rise of global city with multi-ethnic, pluralistic urban societies
- Global access to health care and international education
- Ease of social Interconnectivity…Internet technology, mobile phone
Political Globalization
- Global governance and shared responsibility
- Transparency and political cooperation
How
Growth of politico-economic blocks like EU, G20, G8
Multi-governmental organization to harmonize national economies…IMF, WTO, World Bank
Globalisation has seen the growth of political ideologies e.g. Capitalism and democracy.
It has also seen the growth of dominant countries e.g. U.S. and increasingly China.
Globalisation has probably enabled the emergence of Arab Spring in the Middle East as well as the growth of militia groups such as Al Qaeda.
A note on Arab Spring
is a term for the revolutionary wave of demonstrations and protests (both non-violent and violent), riots, and civil wars in the Arab world that began on 17 December 2010. The Arab Spring is widely believed to have emerged from the dissatisfaction with the rule of local governments, wide gaps in income levels, including issues such as dictatorship or absolute monarchy, human rights violations, political corruption and so on.
Where:
- By December 2013 rulers had been forced from power in Tunisia, Egypt (twice), Libya, and Yemen
- Civil uprisings have erupted in Bahrain and Syria, major protests have broken out in Algeria, Jordan, Kuwait, Morocco, and Sudan …Minor protests have occurred in Mauritania, Oman, Saudi Arabia.
Cultural Globalization
Cultural globalization may include cultural mingling, interaction and assimilation, so called domination of western cultural traits in the form of Americanisation or McDonaldisation. It can also adapt to the local culture through glocalisation, and leads to circulation of ideas, information and innovation and networking in virtual space (face book, twitter etc).
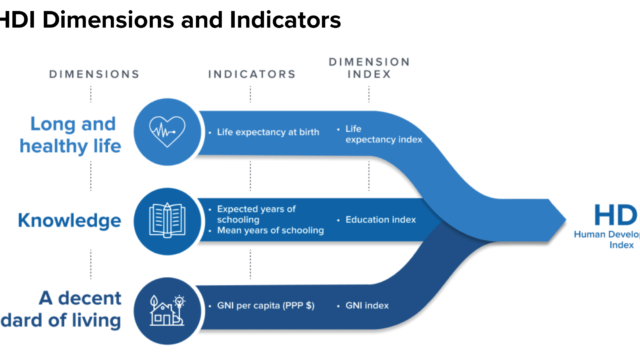
Unit 4. Globalization Indices showing how countries participate in global interactions
Globalization is uneven. Some countries are more connected than others. There is even great disparity with in a country in terms of global connectedness. Degree of global interactions may depend on historical, economic, social, cultural and political factors. One of the well known measures of globalization is AT Kearney World Cities index where the cities have been ranked based on the following indicators.
- Business activities
- Human capital
- Information exchange
- Cultural experience
- political engagement
Refer to the AT Kearney’s 2021 Global Cities Report: Global hub as per the globalization index
The KOF Globalisation Index measures the economic, social and political dimensions of globalisation. Globalisation in the economic, social and political fields has been on the rise since the 1970s, receiving a particular boost after the end of the Cold War.
Find out more on KOF Globalization Index
| Global Superpowers | |
|---|---|
| Superpower | A country or a group of country with significant hard and soft power to project it’s influence globally. |
| Hyper power | A dominant superpower with almost no rival. USA in 1990s after the collapse of the Soviet Union. |
| Demographic superpower | A country with a very large population of more than 100 million. |
| Proxy war | When the superpowers use third party country or group to fight against each other rather than fighting directly. Such as the proxy war between Saudi Arabia and Iran. |
| Failed state | When the superpowers use third party country or group to fight against each other rather than fighting directly. Such as the proxy war between Saudi Arabia and Iran. |
| First global superpower in the modern times | British Empire comprises of the territories and colonies ruled by the United Kingdom between late 16th to early 18th century. The first TNC was the British East India Company |
| Soft power | It signifies the power of persuasion through cultural influences, international authority and decision-making. The Harvard political thinker Joseph Nye coined the term. |
| Hard Power | It signifies application of force by military action, threat, economic sanctions, trade wars and aid policy. |
| Superpower index | Is an attempt to measure superpower based on a few quantitative indicators 1. Economic: Total GDP 2. Demographic: Total population 3.Military: Nuclear warheads 4. Economic and cultural: Fortune Global 500 TNCs, capability to invest in new innovation. |
Concept of the Economic indicators:
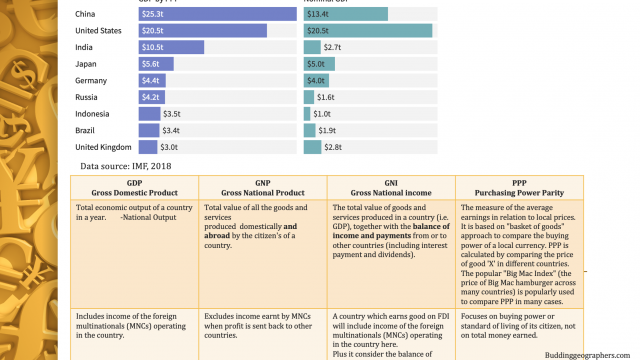
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total economic output of a country in a year. It is the total value of all final goods and services produced within an economy over a period of time, usually a year. GDP is an indicator of the local/national economy.
GDP per capita to understand how the wealth is distributed within the population, however as it is an average, extreme rich and poor will be neutralized by the result. GDP per capita is the total output divided by the total number of people or population, i.e. the average amount of money each person makes.
Gross National Product (GNP): GNP is the total value of all the goods and services produced domestically and abroad by the citizen’s of a country. GNP represents how the nationals of a country are contributing to the country’s economy giving importance to citizenship but overlooks location.
Gross National Income (GNI): The total value of goods and services produced in a country (i.e. GDP), together with the balance of income and payments from or to other countries (including interest payment and dividends). GNI per person provides a better picture of the wealth distribution.
Better solution to GNI measure is to consider GNI at PPP:
Purchasing power parity (PPP): Is the measure of the average earnings in relation to local prices (i.e. how much one can buy in local currency equivalent to 1 dollar). PPP is a macroeconomic approach to compare economic productivity and standards of living between countries. It is based on “basket of goods” approach to compare the buying power of a local currency. The GNI of a country is converted into US dollars on the basis of how the value of a currency can be compared to other countries in relation to the buying power of the currency. PPP is calculated by comparing the price of good ‘X’ in different countries. To make a meaningful comparison of prices across countries, a wide range of goods and services must be considered. The popular “Big Mac Index” (the price of Big Mac hamburger across many countries) is popularly used to compare PPP in many cases.
Analyze on the basis of the super power index: Is China a Super power country?
China is projected to overtake the U.S. as a regional power by 2030. China is already a demographic and economic superpower and has a larger economy than USA. Read this article to understand the superpower dynamics of the world at present. With 6 largest Megacities of the world and one-fifth of the world population, China is a huge market. High growth rate has created a sizable affluent population with sufficient disposable income. China is a leader in Artificial intelligent technology and a home of the fastest growing World Unicorn Startups (companies with more than 1 billion dollar worth). China is also the world leader in renewable energy production. Read World Economic Forum article on China by number to understand the rising power of China.
Class work: Discuss in groups how soft and hard power is influencing global interactions?
Click here to review the list of the largest countries according to the population size
Click here to review the ranking of the countries based on GDP in 2022
Click here to review the list of countries having the highest number of Fortune global 500 companies
Click here to review the list of the unicorn startup companies